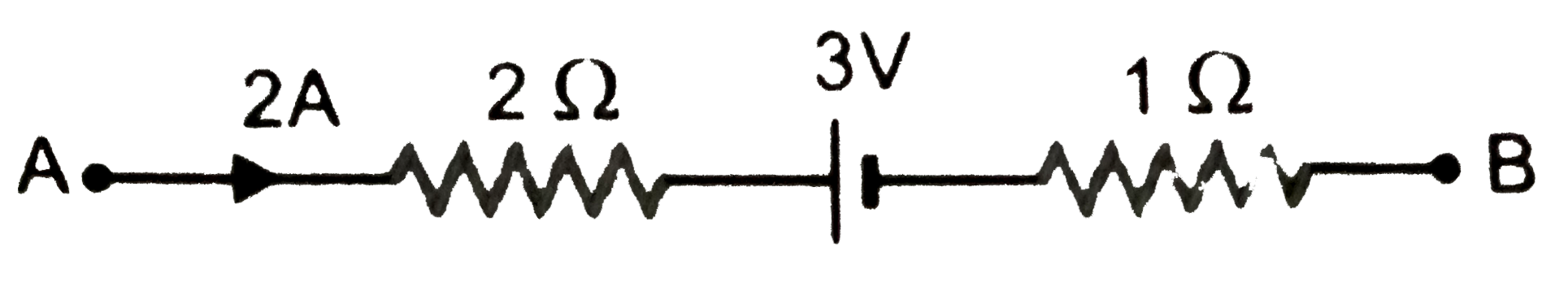Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-CURRENT ELECTRICITY-EX.II
- Figure represents a part of closed circuit. What is the potential diff...
Text Solution
|
- In the Bohr's model of hy drogen atom, the electron moves around the n...
Text Solution
|
- There are three copper wires of length and cross-sectional area (L,A),...
Text Solution
|
- When a piece of aliminium wire of finite length is drawn through a ser...
Text Solution
|
- Every atom makes one free electron in copper. If 1.1 A current is flow...
Text Solution
|
- A metal wire of resistance R is cut into three equal pieces that are t...
Text Solution
|
- Two cells X and Y are connected to a resistance of 10Omega shown in th...
Text Solution
|
- Masses of 3 wires of same metal are in the ratio 1 : 2 : 3 and their l...
Text Solution
|
- As the temperature of a metallic resistor is increased,the product of ...
Text Solution
|
- What will b e the equivalent resistance b etween the A and D?
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement of resistances shown in the circuit, the potential ...
Text Solution
|
- It is observed in a potentiometer experiment that no current passes th...
Text Solution
|
- The resistance across P and Q in the given figure is
Text Solution
|
- When no current is passed through a conductor,
Text Solution
|
- A Steady current flows in a metalic conductor of non uniform cross sec...
Text Solution
|
- Internal resistance of a cell depends on
Text Solution
|
- The resistance of the circuit between A and B is:-
Text Solution
|
- The number of free electrons per 100 mm of ordinary copper wire is 2xx...
Text Solution
|
- The poten tial difference between the terminals of a cells is found to...
Text Solution
|
- What is the reading of ammeter is adjoining circuit diagram.
Text Solution
|
- The following diagram shows the circuit for the comparision of e.m.f. ...
Text Solution
|