A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-TEST PAPERS-PHYSICS
- A block of mass m is being pulled up a rough incline by an agent deliv...
Text Solution
|
- In the question number 66, the charge on capacitors C(1)and C(4) are
Text Solution
|
- In the given LCR series ciruit reading of voltmenter is 120V. The read...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform cylinder of mass M lies on a fixed plane inclined at an angl...
Text Solution
|
- When interference of light takes place
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic field in a certain cylindrical region is changing with ti...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure balls A&B are released simultaneously , when str...
Text Solution
|
- A narrow pipe of length 2m is closed at one end. The velocity of sound...
Text Solution
|
- A very thin sheet of plastic having refractive index mu=1.5 covers one...
Text Solution
|
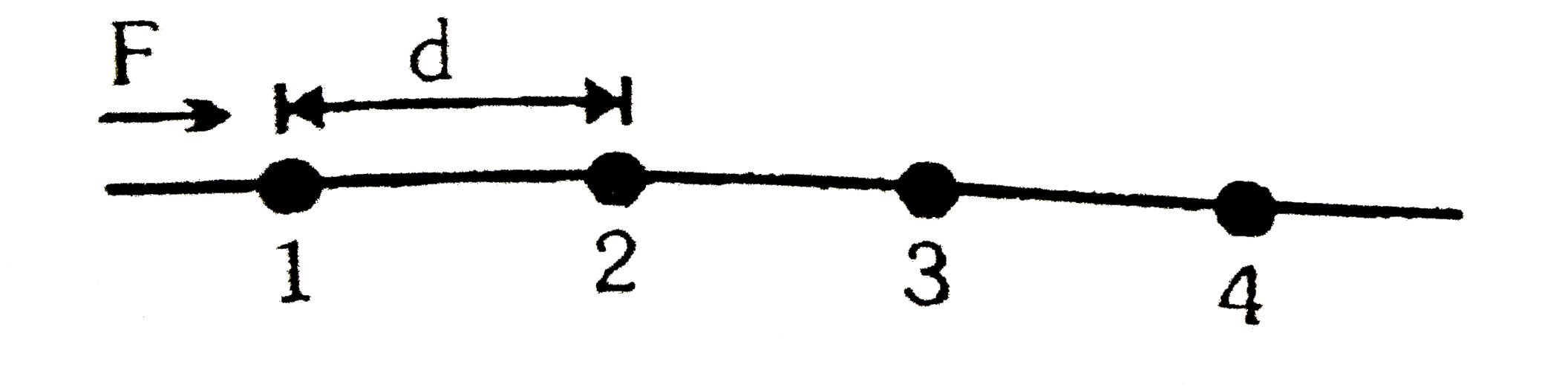
- The Fig. shows a string of equally placed beads of mass m, separated b...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in diagram initial charge on capacitor is zreo . Now switch ...
Text Solution
|
- Three musicians experiment with the Doppler affect . Musician A rides ...
Text Solution
|
- A wave equation which gives the displacement along the y- direction is...
Text Solution
|
- On an inclined plane making an angle theta with the horizontal plane, ...
Text Solution
|
- On an inclined plane making an angle theta with the horizontal plane, ...
Text Solution
|
- In the given circuit switch S(2) is Kept closed and S(1) is kept open ...
Text Solution
|
- In the given circuit switch S(2) is Kept closed and S(1) is kept open ...
Text Solution
|