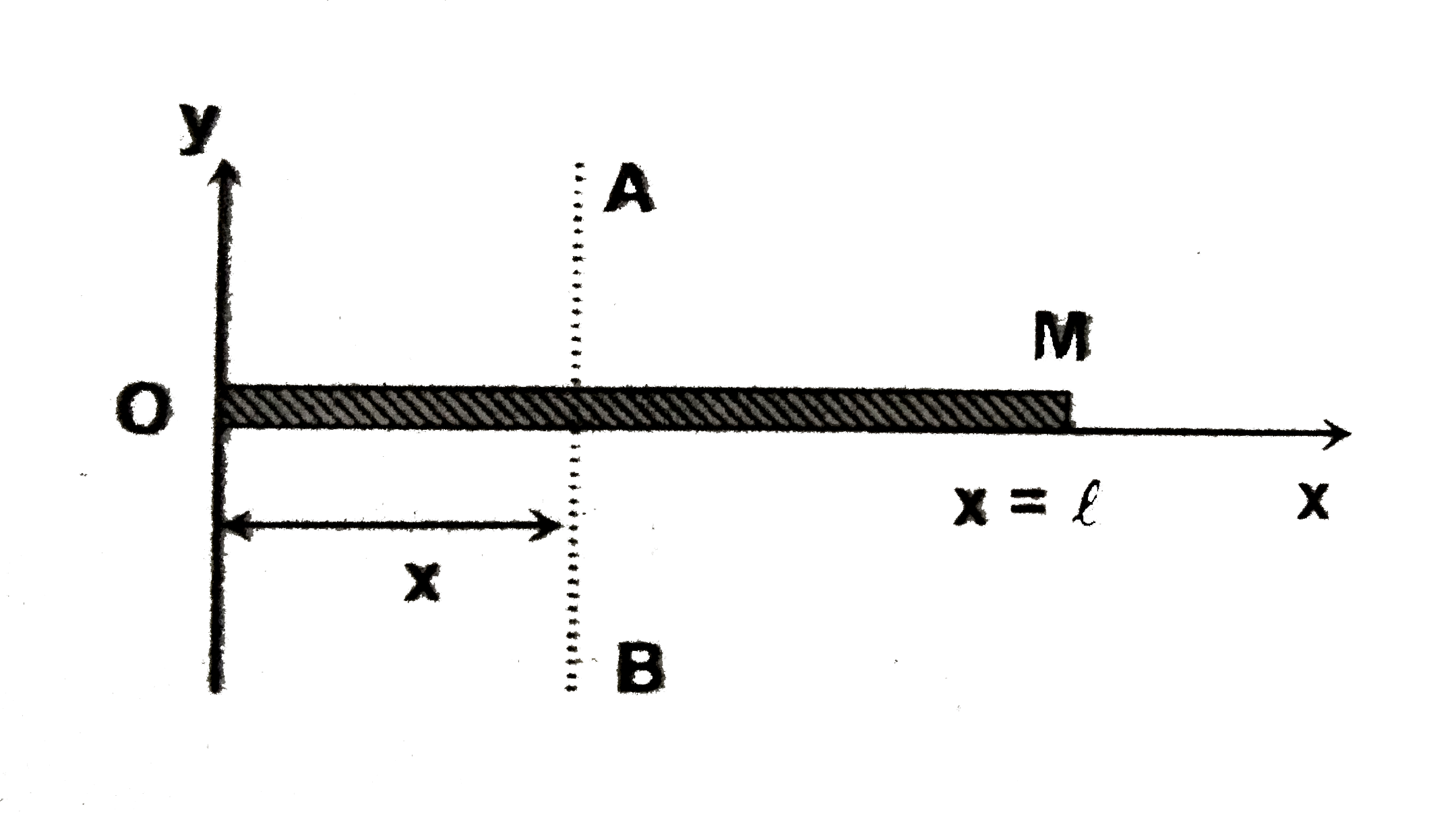
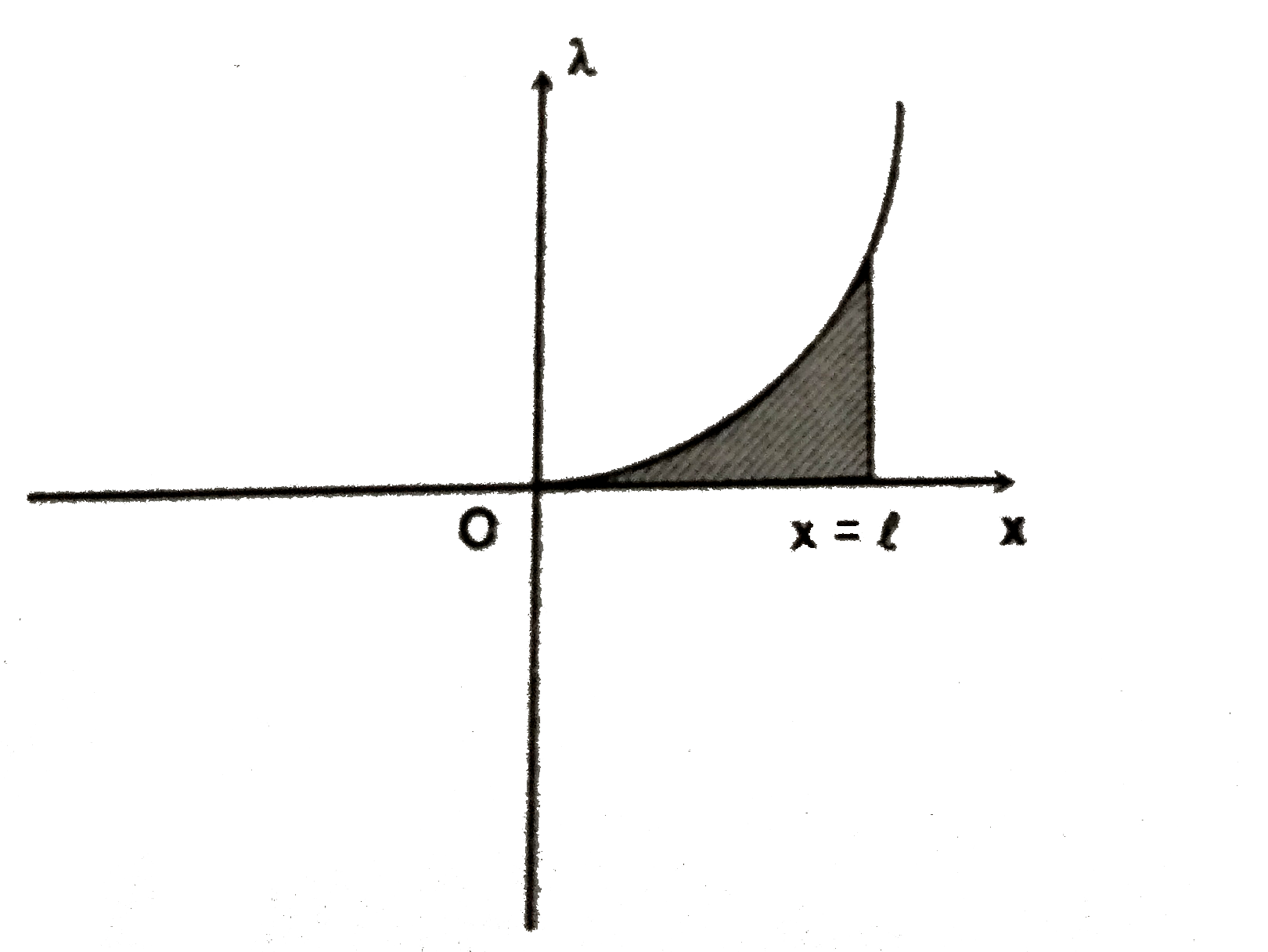
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A non uniform rod OM (of length l m) is kept along x-axis and rotating...
Text Solution
|
- Find the moment of inertia of the rod AB about an axis yy as shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the moment of inertia of a uniform rod of mass M and length ...
Text Solution
|
- The moment of inertia of a thin uniform rod of mass M and length L abo...
Text Solution
|
- The moment of inertia of a thin rod of mass M and length L about an ax...
Text Solution
|
- एक पतली छड़ का द्रव्यमान M तथा लम्बाई l है। छड़ के एक सिरे से l//3 दूरी ...
Text Solution
|
- A non–uniform thin rod of length L is placed along x-axis as such its ...
Text Solution
|
- Mass M is distributed over the rod of length L. If linear mass density...
Text Solution
|
- The moment of inertia of a thin uniform rod of mass M and length L abo...
Text Solution
|