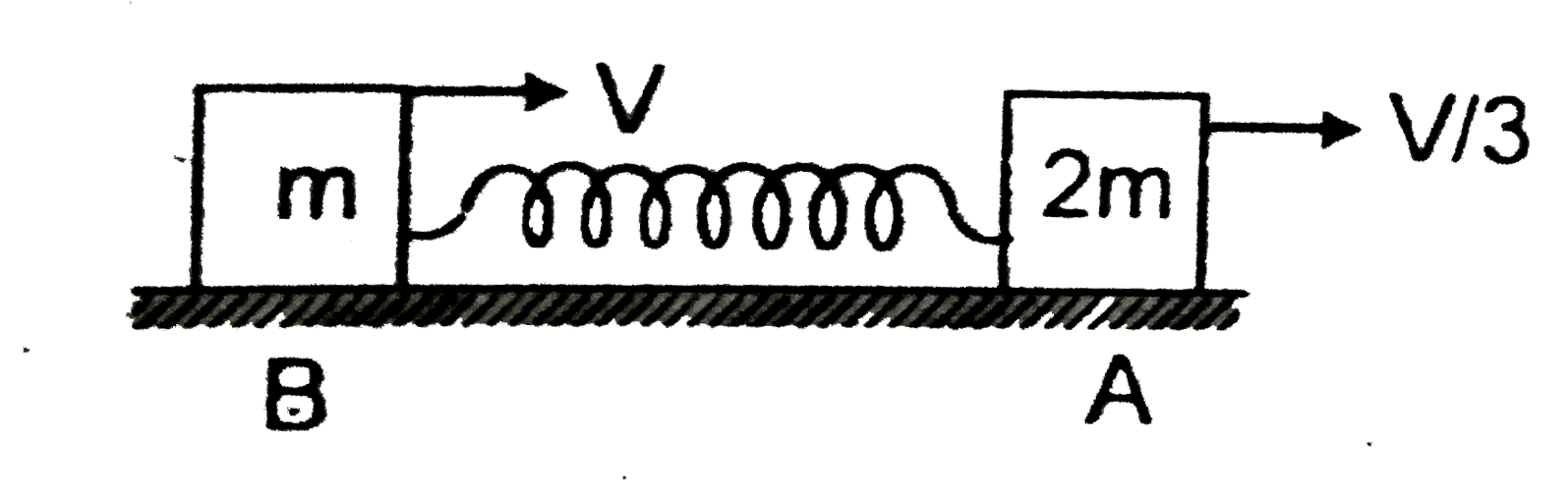
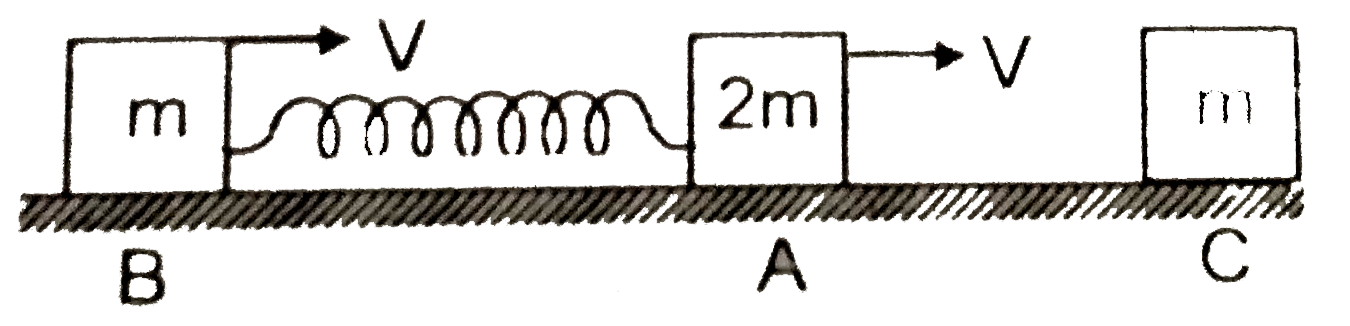A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Two blocks A and B of mass 2 m and m respectively are connected to a m...
Text Solution
|
- The block of mass M moving on the frictionless horizontal surface col...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical blocks A and B , each of mass m resting on smooth floor ...
Text Solution
|
- Block C of mass M is moving with velocity V(0) and collides elasticall...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and B of mass 2m and m respectively are connected to a ma...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is initially moving to the right on a horizontal fri...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m moving with velocity v(0) on a smooth horizontal sur...
Text Solution
|
- A mass m moves with a speed v on a horizontal smooth surface and colli...
Text Solution
|
- M द्रव्यमान का एक गुटका जो घर्षणशील क्षैतिज सतह पर गति कर रहा है K स्...
Text Solution
|