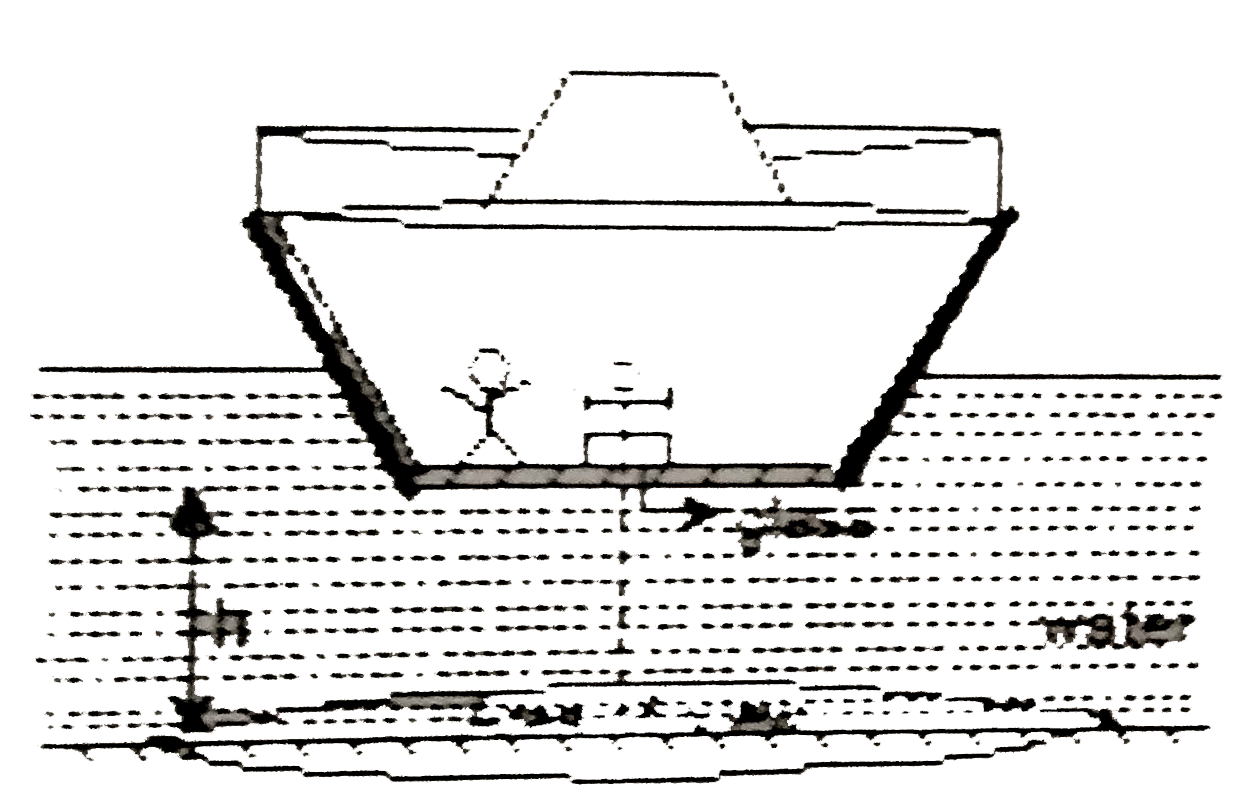
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A glass slab of diameter D=20cm is made at the base of a ship as shown...
Text Solution
|
- The time required to pass the light through a glass slab of 2 mm thick...
Text Solution
|
- A man stands on a glass slab of height h and inside an elevator accele...
Text Solution
|
- White light is incident normally on a glass slab. Inside the glass sla...
Text Solution
|
- A glass prothole is made at the botton of a ahip for observing sea lif...
Text Solution
|
- A monochromatic rar is incident on a glass slab with glancing angle 30...
Text Solution
|
- Concept related to Apparant depth & Glass slab
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light grazes the top surface of a glass slab. Can it be trace...
Text Solution
|
- n transparent slabs are arranged one on top of each other. The refract...
Text Solution
|