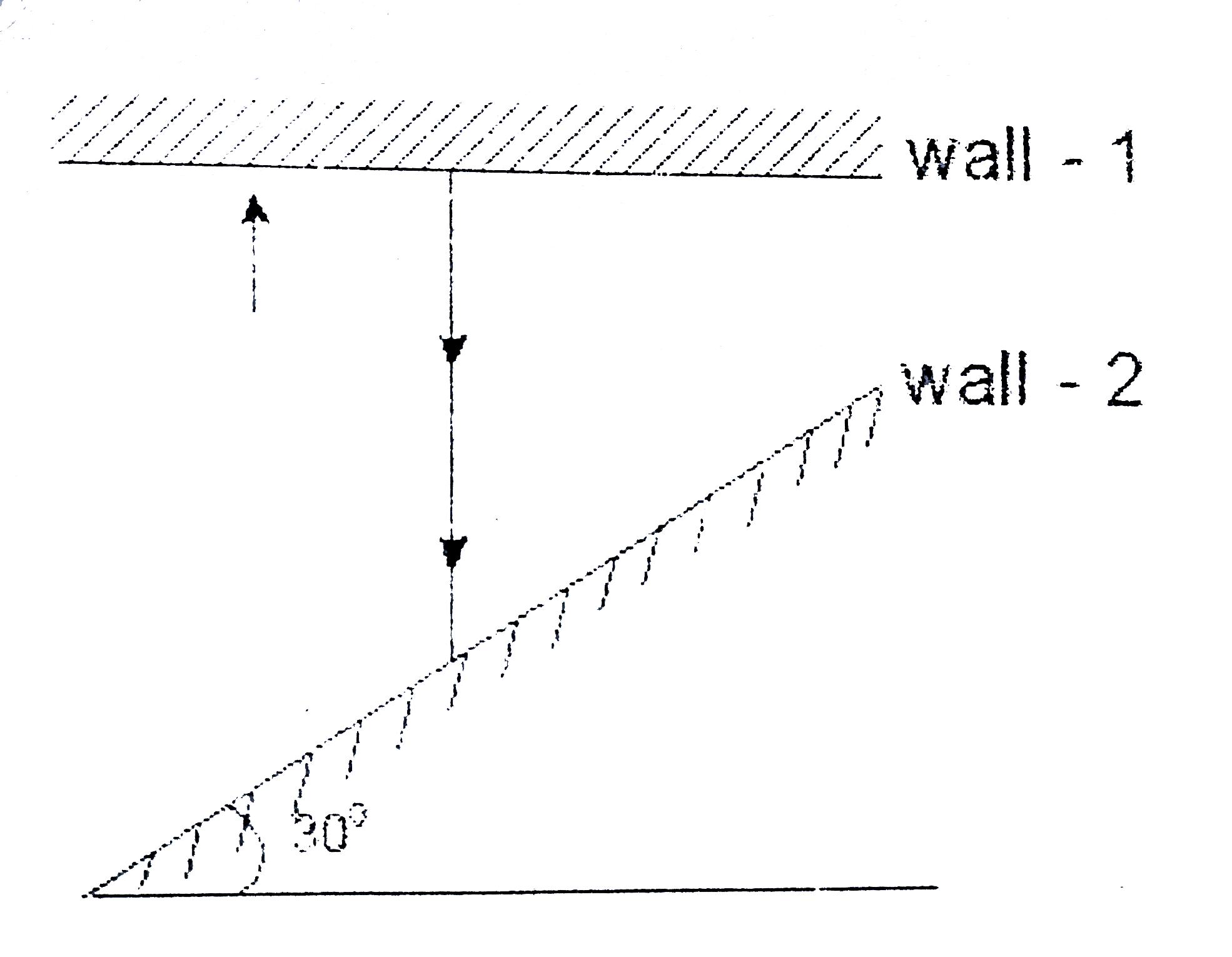
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Molecule of a gas in a container hits one wall (1) normally and reboun...
Text Solution
|
- A molecules in a gas container hits the wall with speed 200m // s at a...
Text Solution
|
- If gas molecules undergo, inelastic collision with the walls of the co...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of number of collisions per second at the walls of container...
Text Solution
|
- If gas molecules undergo, inelastic collision with the walls of the co...
Text Solution
|
- A molecule in a gas container hits a horizontal wall with a speed of 2...
Text Solution
|
- Ideal gas molecules experiences -Elastic collisions with walls of co...
Text Solution
|
- A molecule in a gas container hits a horizontal wall with a speed of 2...
Text Solution
|
- A molecule in a gas container hits a horizontal wall with speed 200 ms...
Text Solution
|