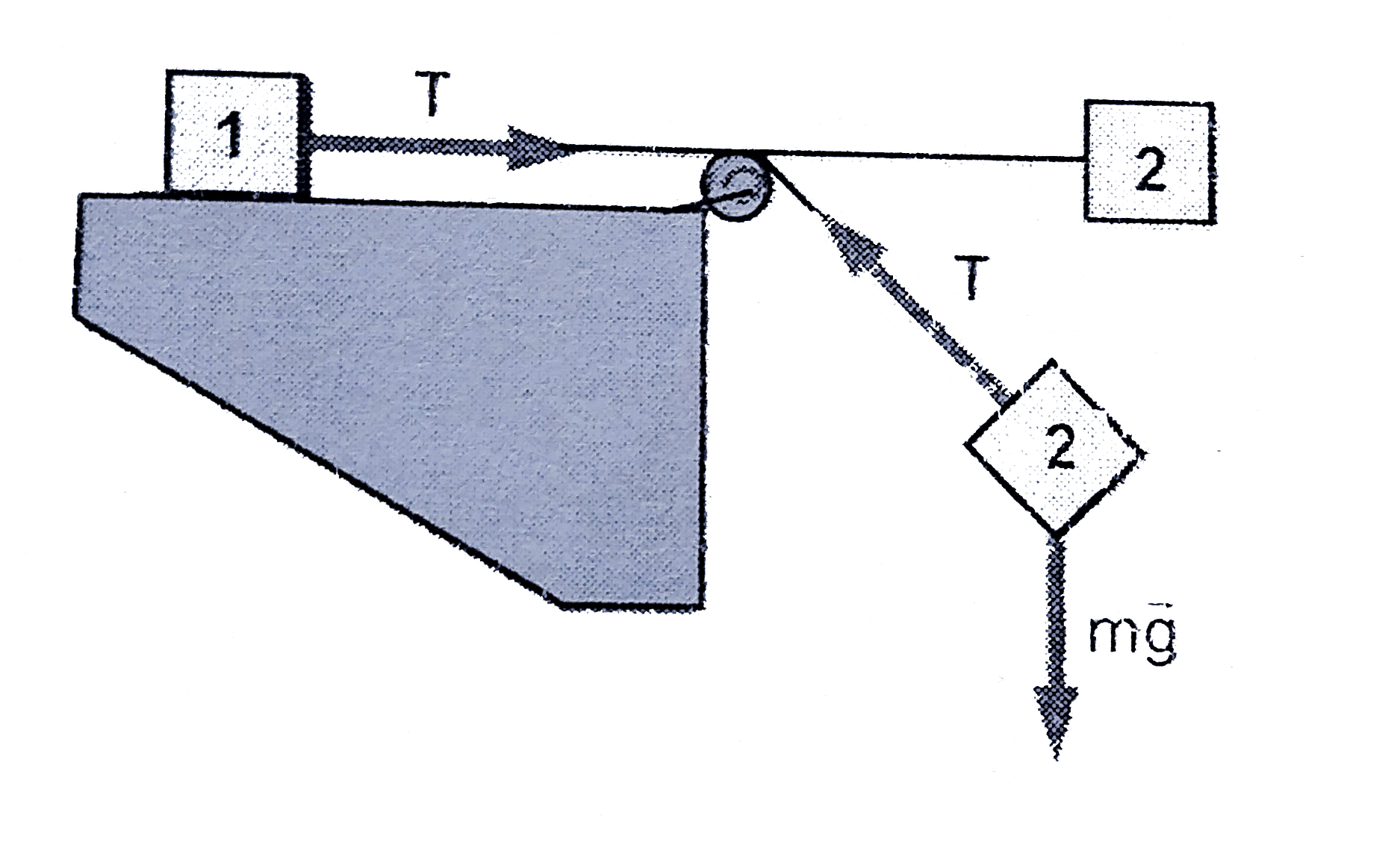
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Two identical blocks are attached by a massless string running over a ...
Text Solution
|
- Two block A and B each of same mass are attached by a thin inextensibl...
Text Solution
|
- A 4 kg block is on a smooth horizontal table. The block is connected t...
Text Solution
|
- In the following arrangement, the system is initially at rest. The 5-k...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks are connected by an inextensible light string, the string i...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows an arrangement of pulleys and two blocks. All surfaces ar...
Text Solution
|
- In the system shown in the figure all surfaces are smooth, pulley and ...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks are connected by a string that passes over a pulley of radi...
Text Solution
|
- The two blocks shown in figure-2.200 are initially at rest. Assuming i...
Text Solution
|