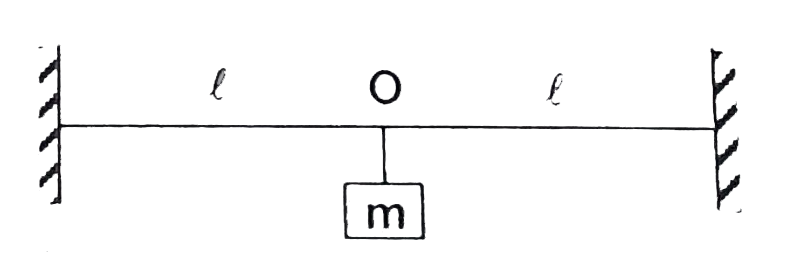
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A steel wire of negligible mass, length 2I, cross sectional area 'A' a...
Text Solution
|
- Rigidity modulus of steel is eta and its Young's modulus is Y. A piece...
Text Solution
|
- A steel of area of cross-section A and length 2L is calmped family bet...
Text Solution
|
- Two wires have identical lengths and areas of cross-section are suspen...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass M is suspended from a wire of length L, area of cross-...
Text Solution
|
- Young's modulus of steel is Y and its rigidity modulus is eta . A piec...
Text Solution
|
- A mass (m) is suspended at the end of a weightless wire of length L, c...
Text Solution
|
- A mass (m) is suspended at the end of a weightless wire of length L, c...
Text Solution
|
- A bar of mass m and length l is hanging from point A as shown in the f...
Text Solution
|