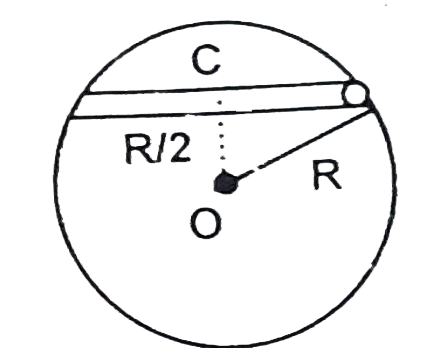
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A tunnel is dug across the earth of mass 'M' and radius 'R' at a dista...
Text Solution
|
- A tunnel is dug along a diameter of the earth. Find the force on a par...
Text Solution
|
- A diametrical tunnel is dug across the earth. A ball dropped into the ...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth tunnel is dug along the radius of the earth that ends at the ...
Text Solution
|
- What impulse need to be given to a body of mass m, released from the s...
Text Solution
|
- A tunnel is dug across the diameter of earth. A ball is released from ...
Text Solution
|
- After drilling a tunnel from surface of earth to the centre, a body of...
Text Solution
|
- A tunnel is dug through the centre of the earth. Show that a body of m...
Text Solution
|
- A tunnel is dug along a diameter of the earth. Find the force in on a ...
Text Solution
|