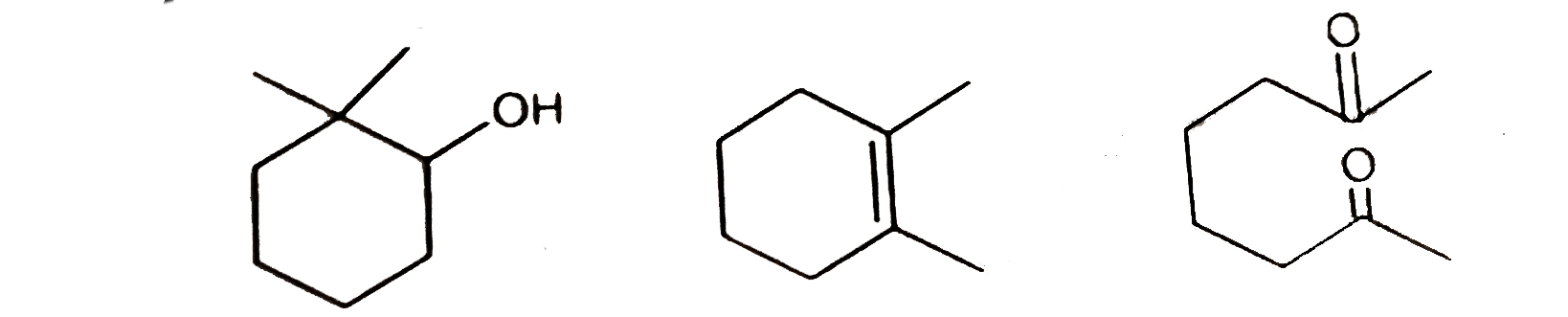
A
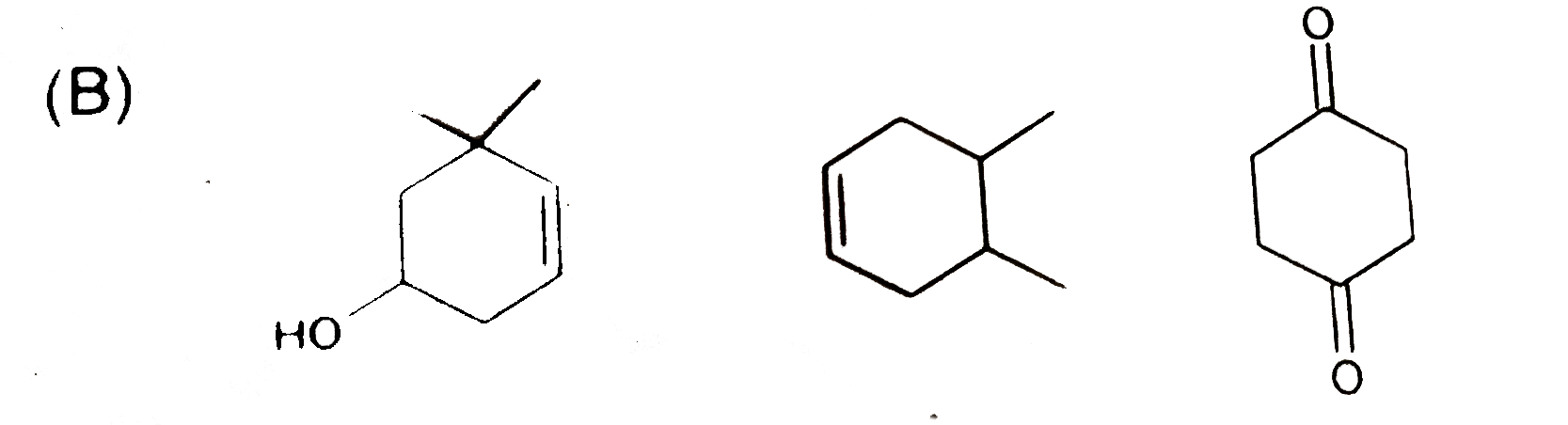
B
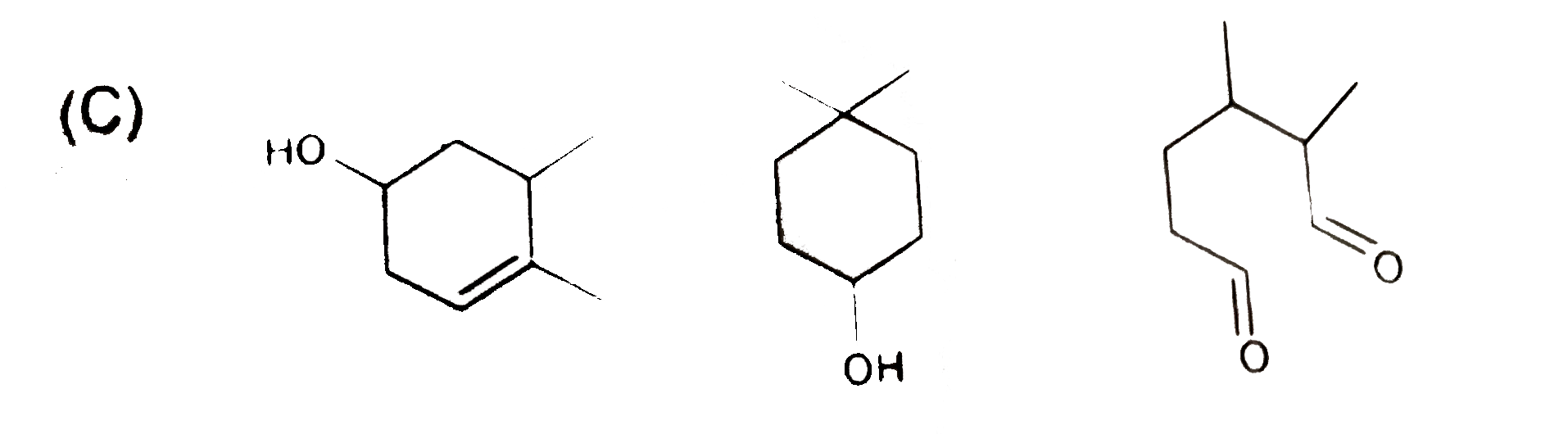
C
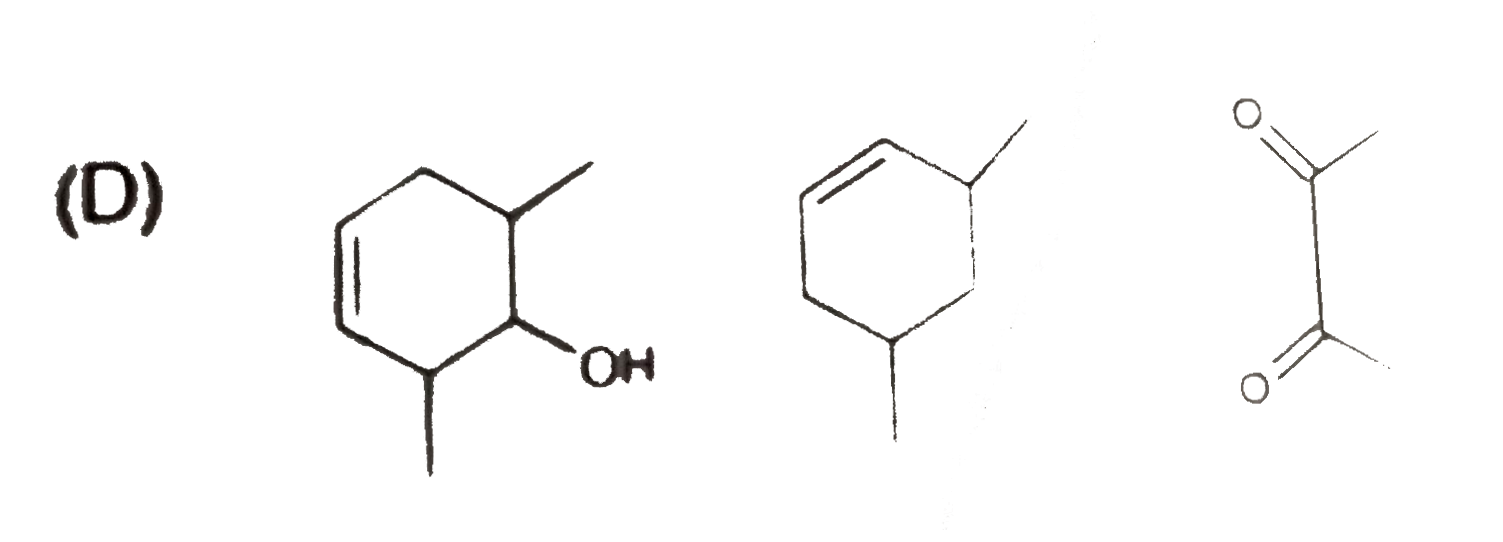
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A compound 'D' (C(8)H(16)O) has following observation (a) It reacts ...
Text Solution
|
- ZnCI(2)+NaHCO(3)overset("Heat")rarr (A)overset("Heat")rarr (B)+(C )+H(...
Text Solution
|
- "Colemanite" + Na(2)CO(3) overset("Fused")rarr (A) + (B) + CO(2) under...
Text Solution
|
- "Colemanite" + Na(2)CO(3) overset("Fused")rarr (A) + (B) + CO(2) und...
Text Solution
|
- (A) (C(8)H(14))underset(Acidic KMnO(4))overset([O])(rarr)(B)+(C )+(D) ...
Text Solution
|
- C(6) H(5) (CH(2))(5) overset(O)overset(||)(C) - Cl underset(CS(2))over...
Text Solution
|
- A compound (A) with molecular formula C(4)H(10)O reacts rapidly with m...
Text Solution
|
- 2 mole 'ic' acid of sulphur overset(-H(2)O)rarr compound 'X' Compoun...
Text Solution
|
- C8H8Cl2(A)overset("Aq. NaoH")rarr(B)overset("Mild reduction")rarr(C)ov...
Text Solution
|