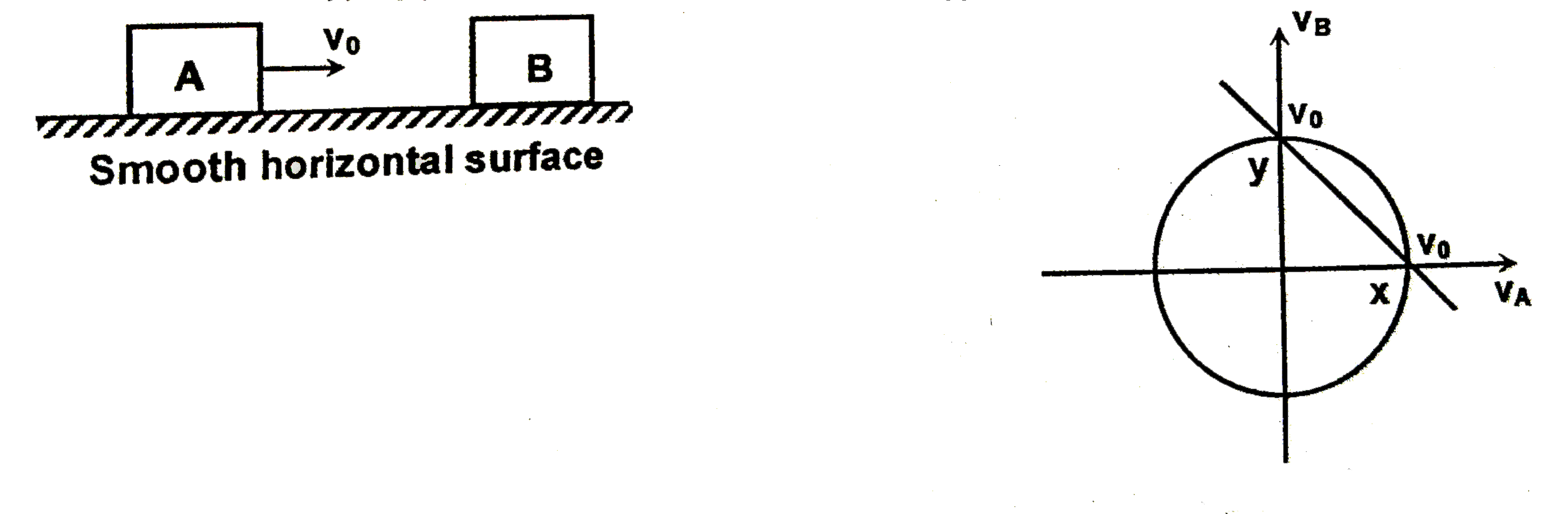
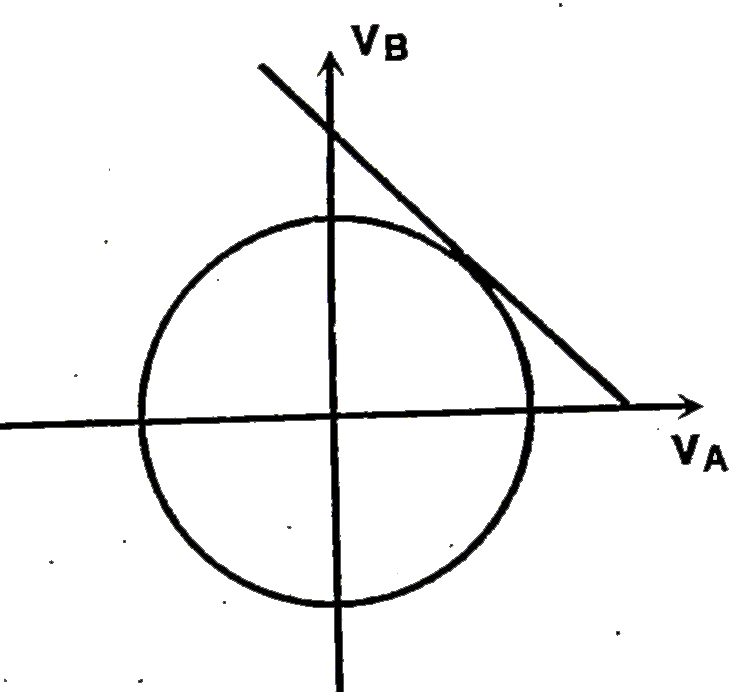
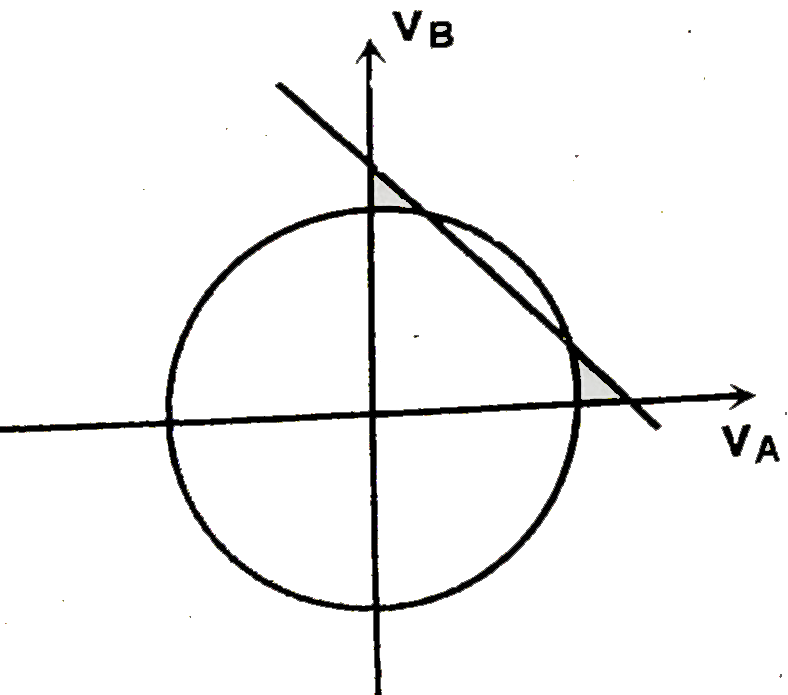
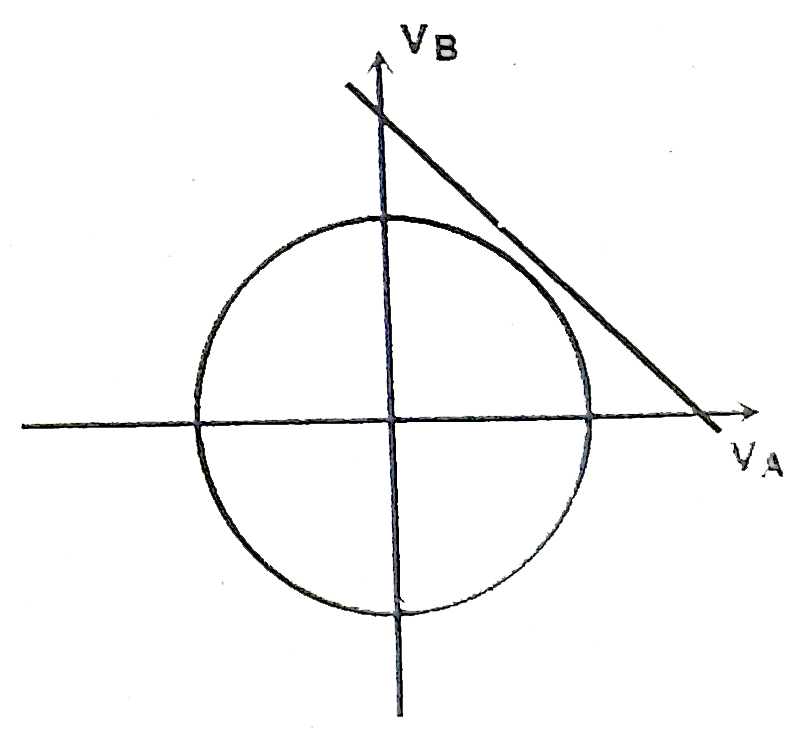
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Graphical soluton of a two body head on collision A block A of mass ...
Text Solution
|
- In fig., blocks A and B move with velocities v(1) and v(2) along horiz...
Text Solution
|
- Three block 1, 2 and 3 are arranged as shown in the figure. The veloci...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m moving with velocity v(0) collides with sphere of...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation as shown in the diagram. The bullet penetrates ...
Text Solution
|
- Graphical soluton of a two body head on collision A block A of mass ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball moving with velocity V(0) , makes a head on collision with anot...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m moving with a velocity v(0) on a smooth horizontal s...
Text Solution
|
- Sphere A of mass 'm' moving with a constant velocity u hits another st...
Text Solution
|