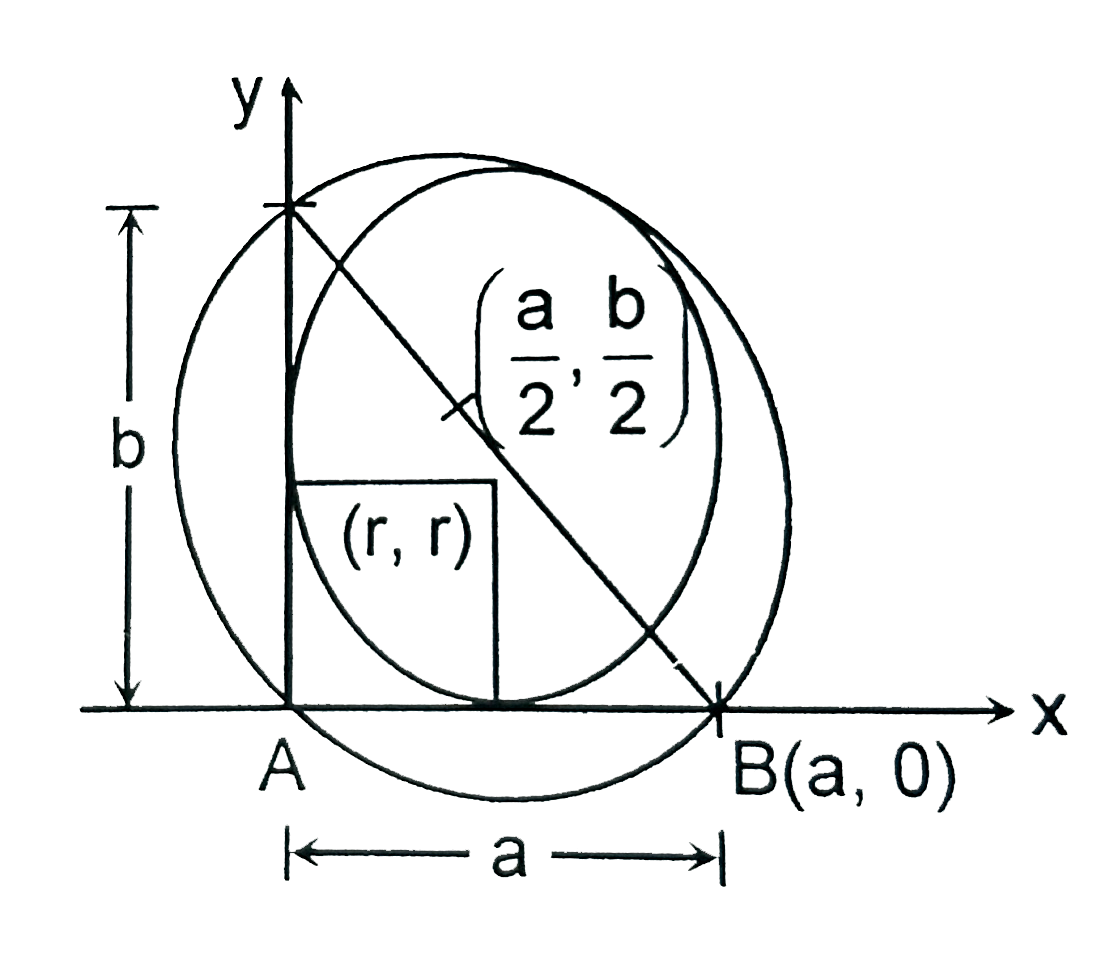A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Let A B C be a triangle right-angled at Aa n dS be its circumcircle. L...
Text Solution
|
- Let C,C1,C2 be circles of radii 5,3,2 respectively. C1 and C2, touch e...
Text Solution
|
- Two circles having radii r1 and r2 passing through vertex A of triangl...
Text Solution
|
- In a right angle triangle with sides a,b,c,a circle is drawn inside is...
Text Solution
|
- Let A B C be a triangle right-angled at Aa n dS be its circumcircle. L...
Text Solution
|
- Three circles,each of radius one,have centres at A,B and C. Circles A ...
Text Solution
|
- C1 and C2 are fixed circles of radii r1 and r2 touches each other exte...
Text Solution
|
- Two circle S1=0,S2=0 of equal radius 'r' intersect such that one circl...
Text Solution
|
- Let two circles S1=0 and S2=0 intersect at point A and B . L1=0 is the...
Text Solution
|