Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
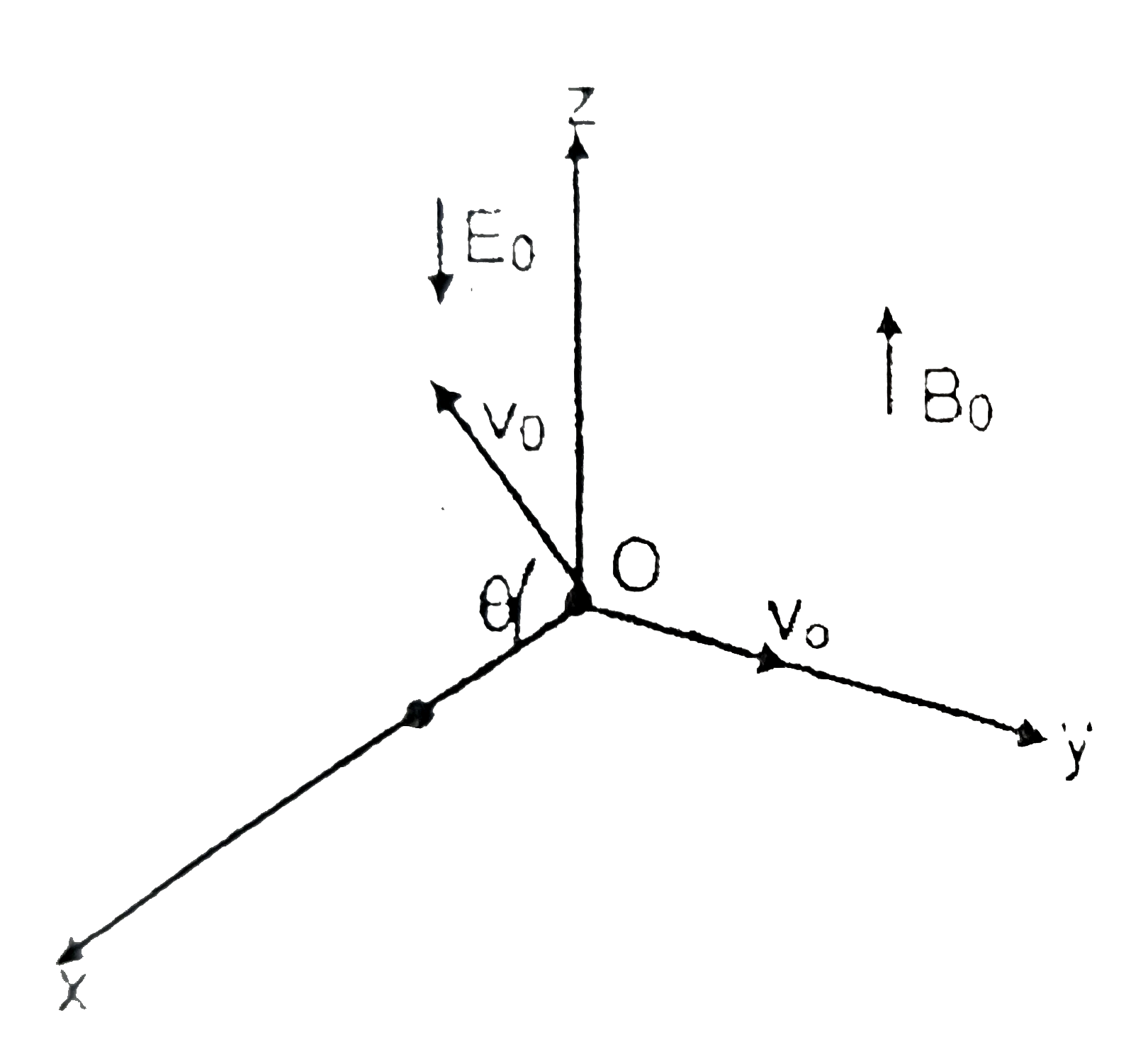
- A charged point particle having positive charge q, mass m is projected...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of charge q(0) and of mass m(0) is projected along the y -a...
Text Solution
|
- Magnetic field exist in the space and given as vecB=-(B(0))/(l^(2))x^(...
Text Solution
|
- In the region between the plane z=0 and z=a (a gt 0) , the uniform ele...
Text Solution
|
- In the region between the plane z=0 and z=a (a gt 0) , the uniform ele...
Text Solution
|
- In the region between the plane z=0 and z=a (a gt 0), the uniform elec...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m and having a positive charge q is projected from ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform magnetic field B=B(0)hatj exists in space. A particle of mas...
Text Solution
|
- A positive charge particle to charge q& mass m is released at origin....
Text Solution
|