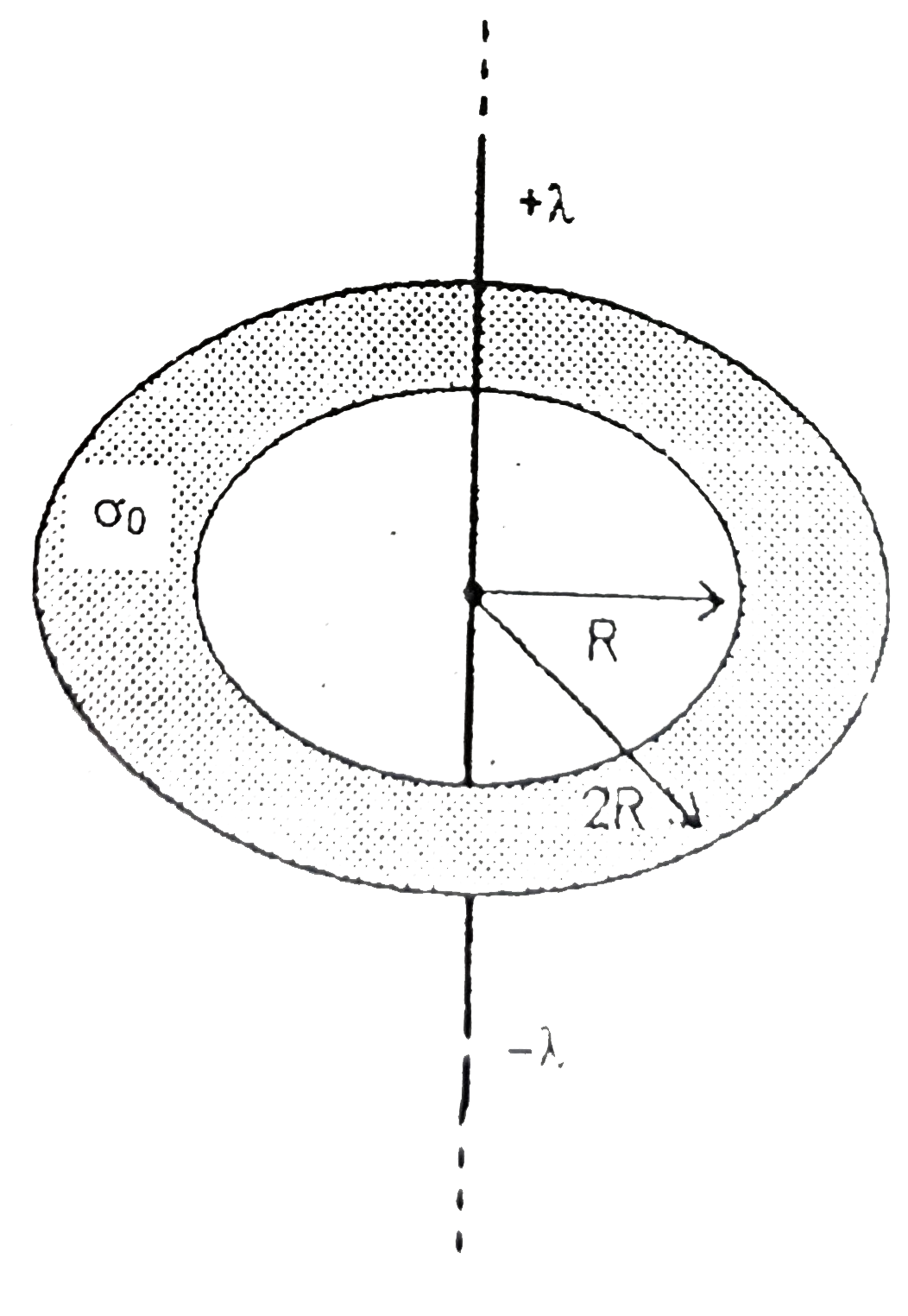
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A non conducting infinite rod is placed along the z-axis the upper hal...
Text Solution
|
- A large sheet carries uniform surface charge density sigma . A rod of ...
Text Solution
|
- For an infinite line of charge having linear charge density lambda lyi...
Text Solution
|
- A semi-infinite insulating rod has linear charge density lambda . The ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the potential at a point on the perpendicular bisector of un...
Text Solution
|
- Find electric field at point A, B, C, D due to infinitely long uniform...
Text Solution
|
- Find the electric field and potential at the centre of curvature of a ...
Text Solution
|
- A non–uniform thin rod of length L is placed along x-axis as such its ...
Text Solution
|
- Find ratio of electric at point A and B. Infinitely long uniformly cha...
Text Solution
|