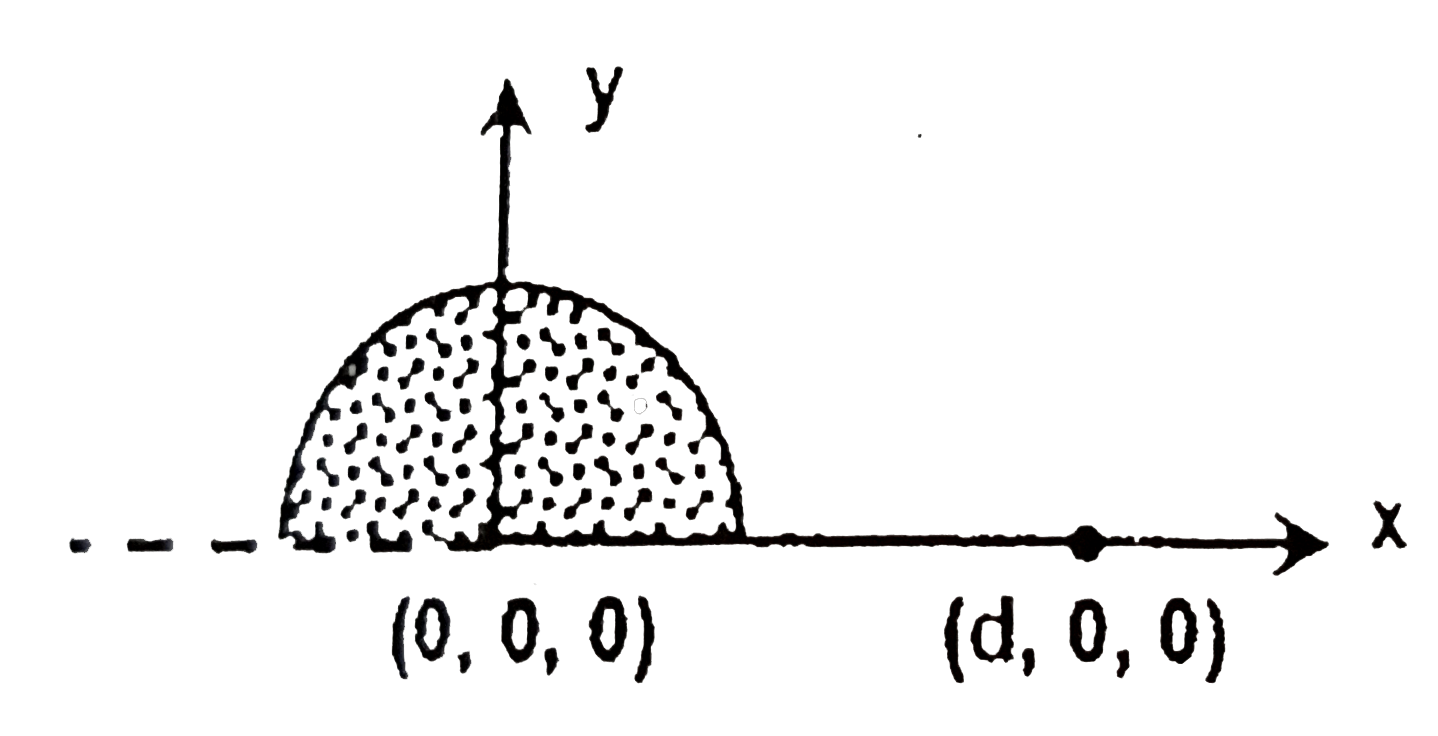A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A solid hemispherical uniformly charged body having charge Q is kept s...
Text Solution
|
- The maximum electric field at a point on the axis of a uniformly charg...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a uniformly charges hemispherical shell. The direction of...
Text Solution
|
- Find electric field at point A, B, C, D due to infinitely long uniform...
Text Solution
|
- The maximum electric field at a point on the axis a uniformly charged ...
Text Solution
|
- 3 charges are placed in a circle of radius d as shown in figure. Find ...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of length L= 20 cm is bent into a semicircular arc and the two ...
Text Solution
|
- There is one non-conducting uniformly charged hemispherical body, whic...
Text Solution
|
- Two positive and two negative charges are kept in x-y plane in free sp...
Text Solution
|