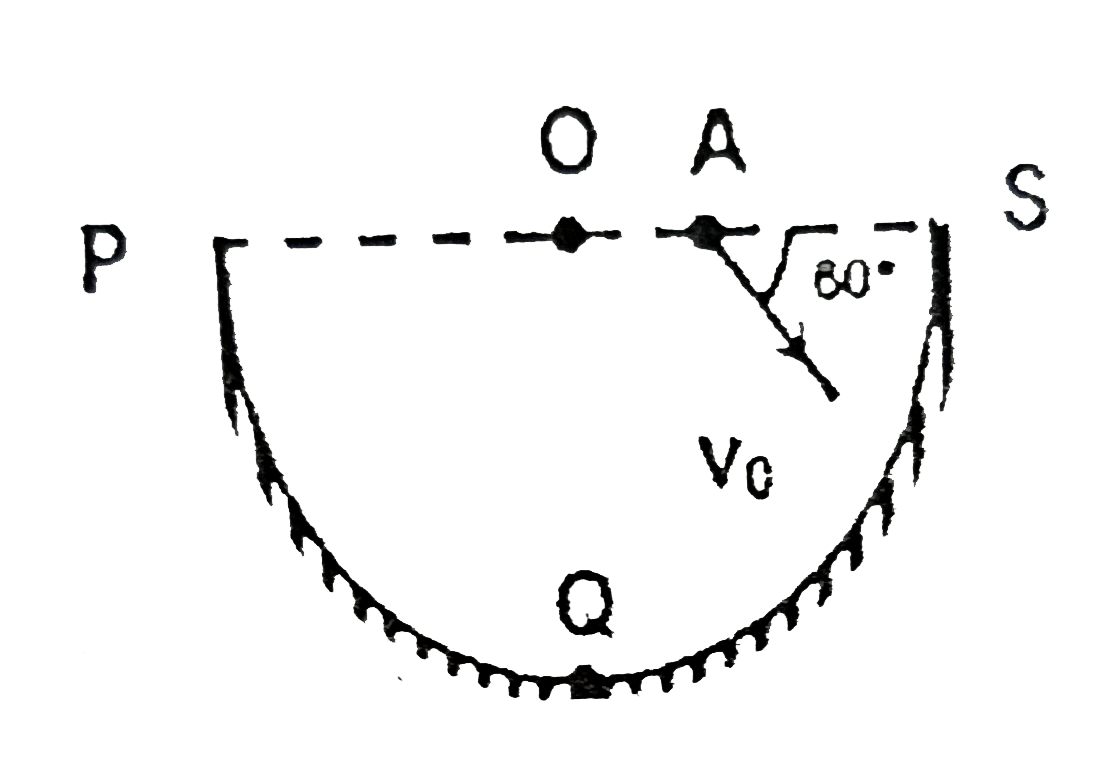A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
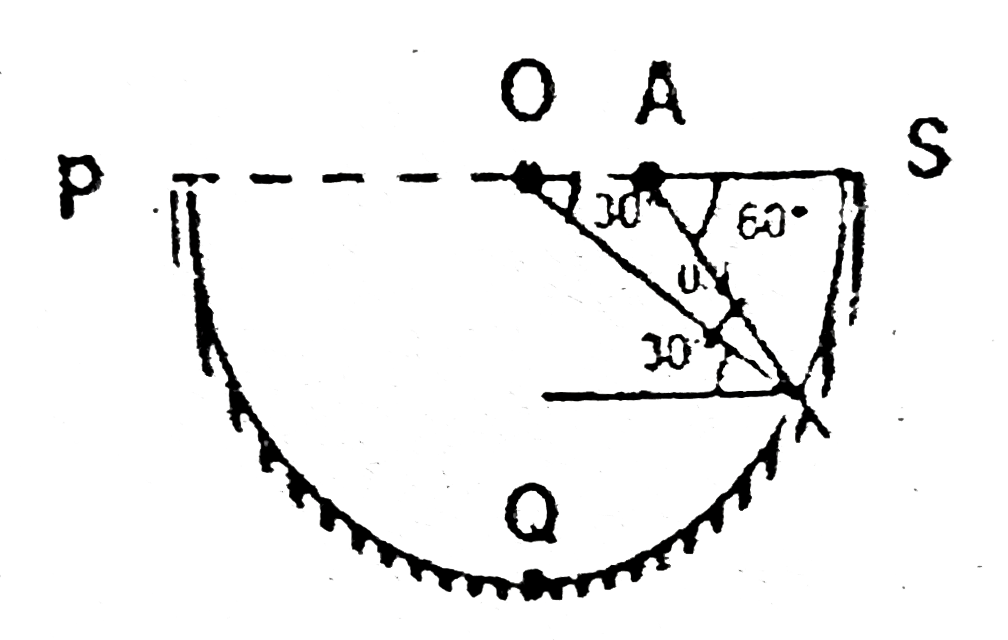
- A ball is thrown from point A making an angle 60^(@) with line OAS as ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball strikes a wall with a velocity vecu at an angle theta with the ...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth tunnel is dug along the radius of the earth that ends at the ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped vertically from a height of 3.6 m. It rebounds from ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped on a horizontal surface from height h. If it rebound...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped on a horizontal surface from height h. If it rebound...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped from height of Im. If coefficient of restituion betw...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped from height of 1m. If coefficient of restituion betw...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped from a heght of 3.6 m and strikes a horizontal su...
Text Solution
|