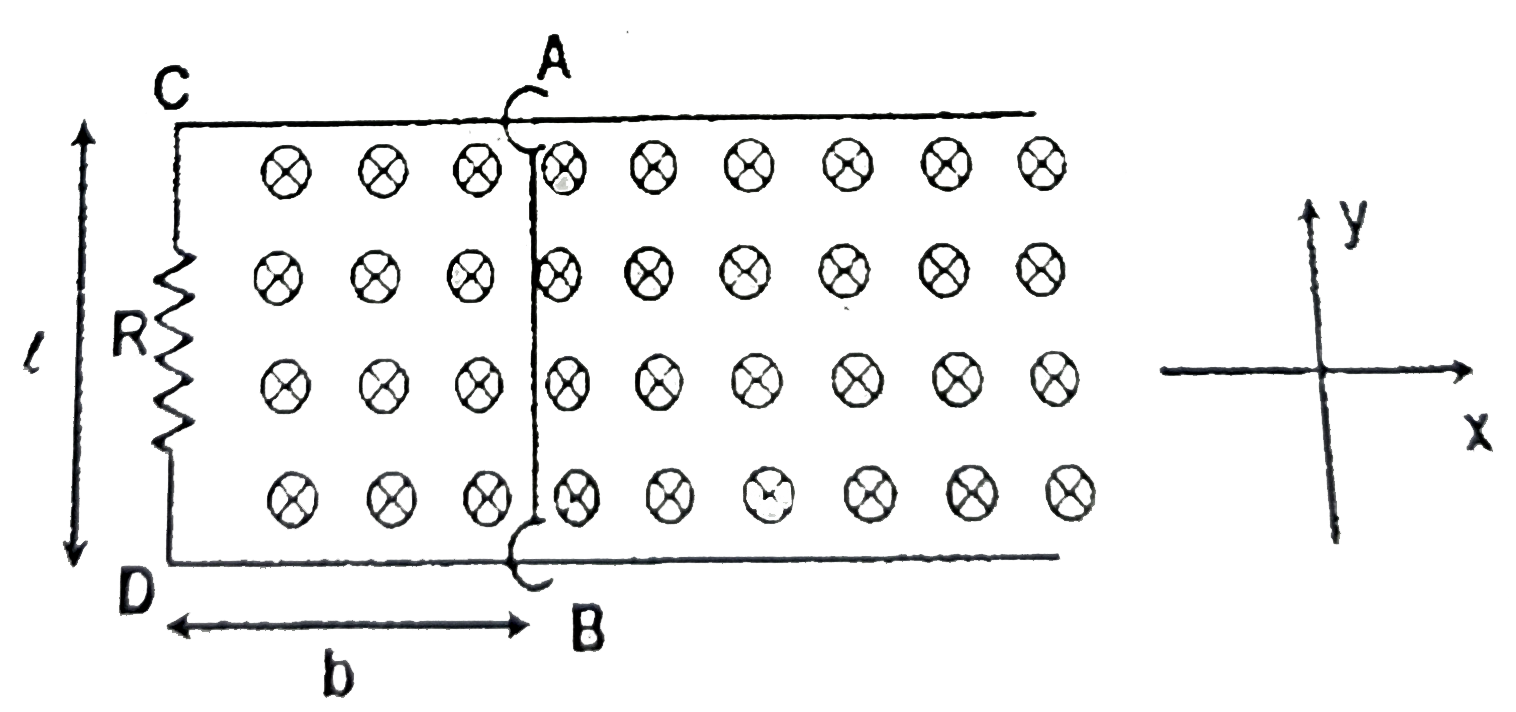
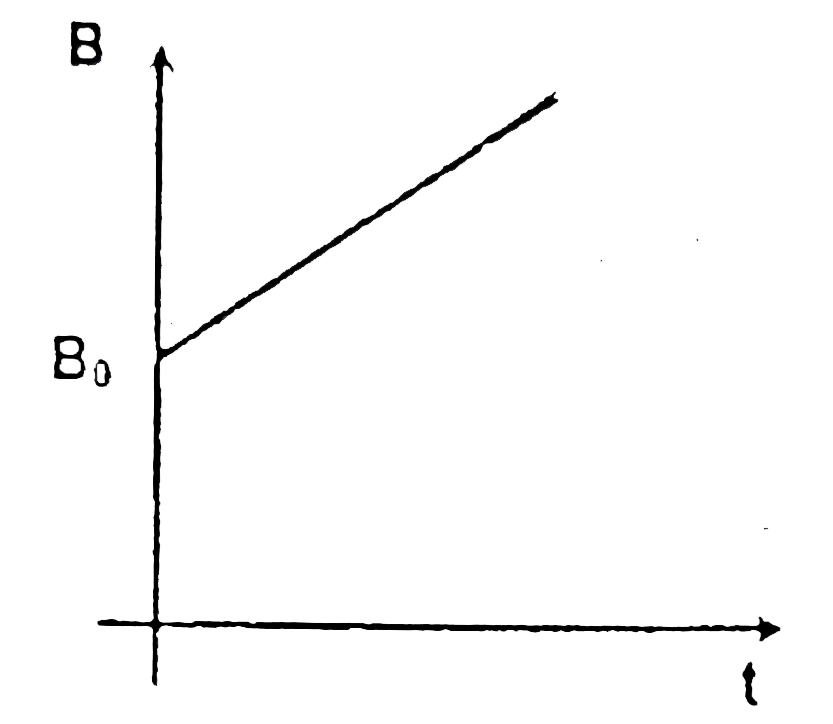
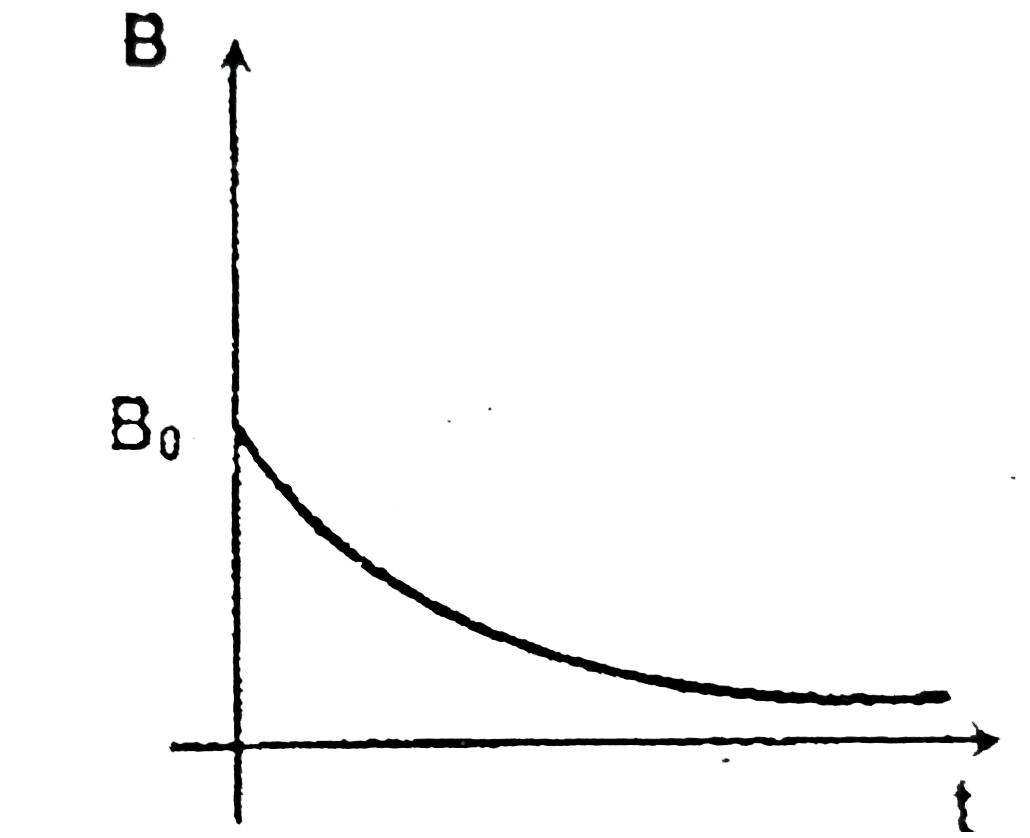
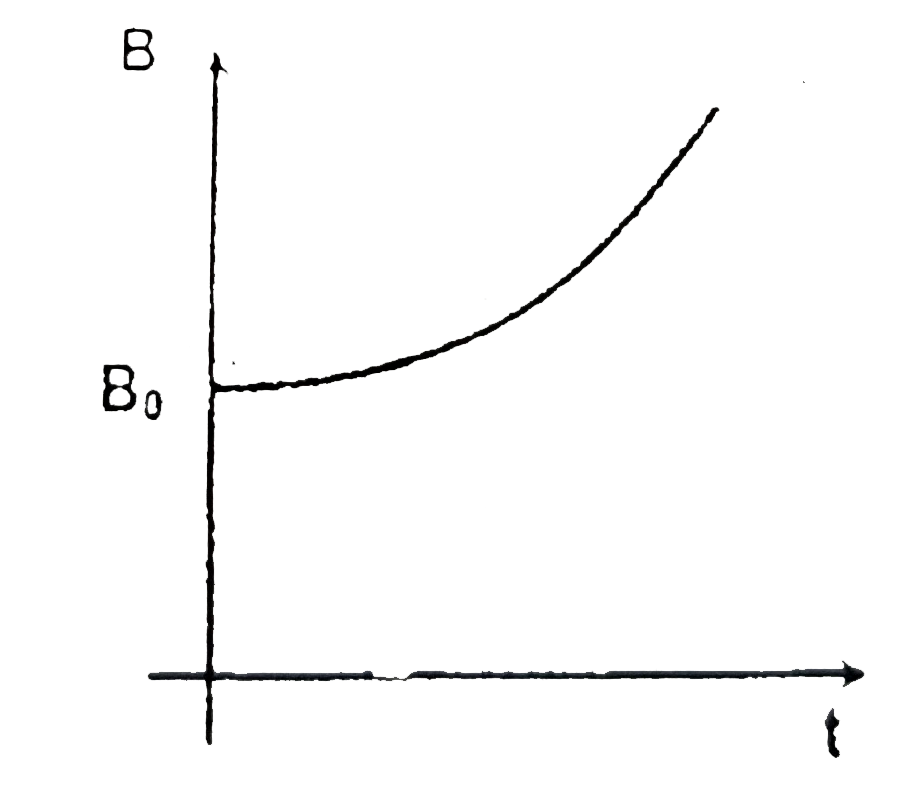
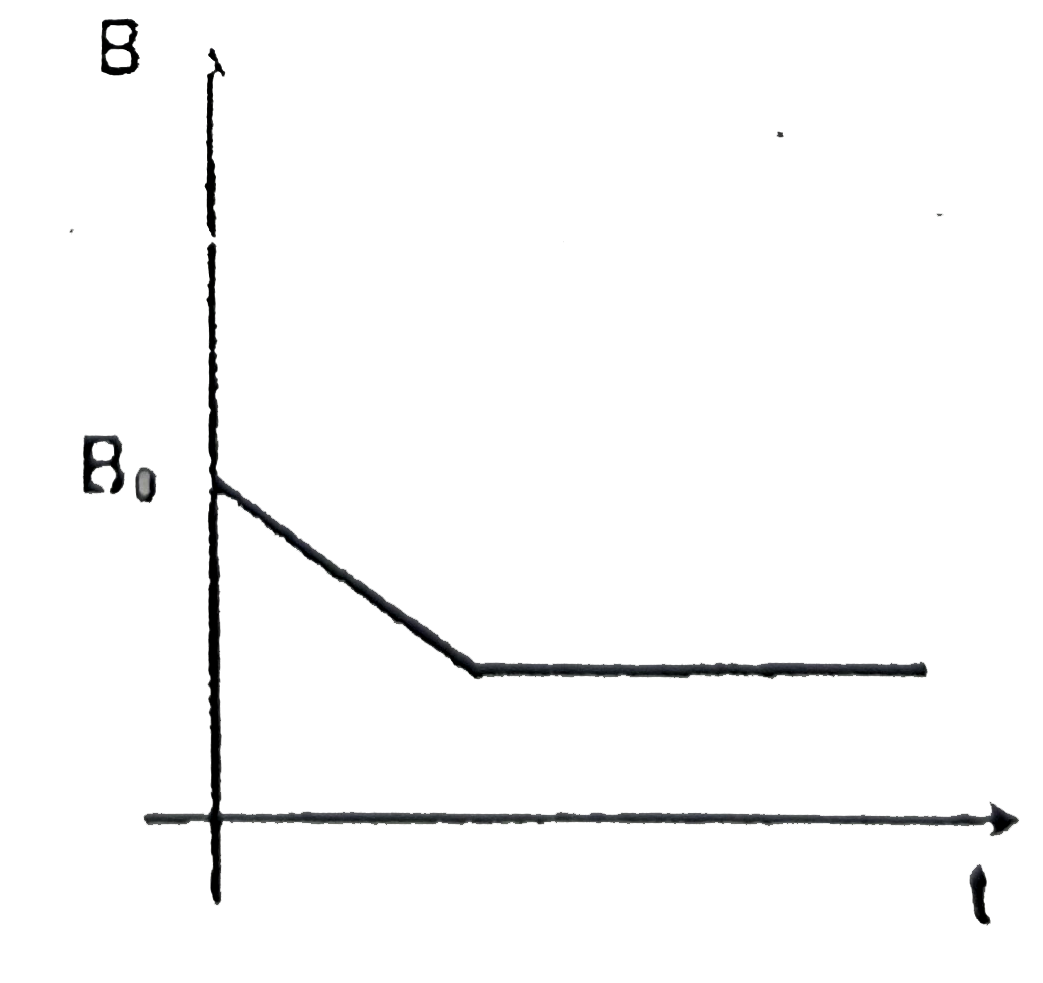
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A conducting movable rod AB lies across the frictionless parallel cond...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting bar mass m and length l moves on two frictionless paralle...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod AB moves parallel to x-axis in the x-y plane. A unifo...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod AB of mass m and length l is placed over two smooth cond...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic field in a region is given by vecB=B(0)/Lxhatk where L is...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod AB is moving parallel to the positive x-axis. A magne...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod of length L lies in X - Y plane and makes an angle 30...
Text Solution
|
- A small conducting rod of length l, moves with a uniform velocity v in...
Text Solution
|
- Two long parallel metallic wires with a resistance 'R' from a horizont...
Text Solution
|