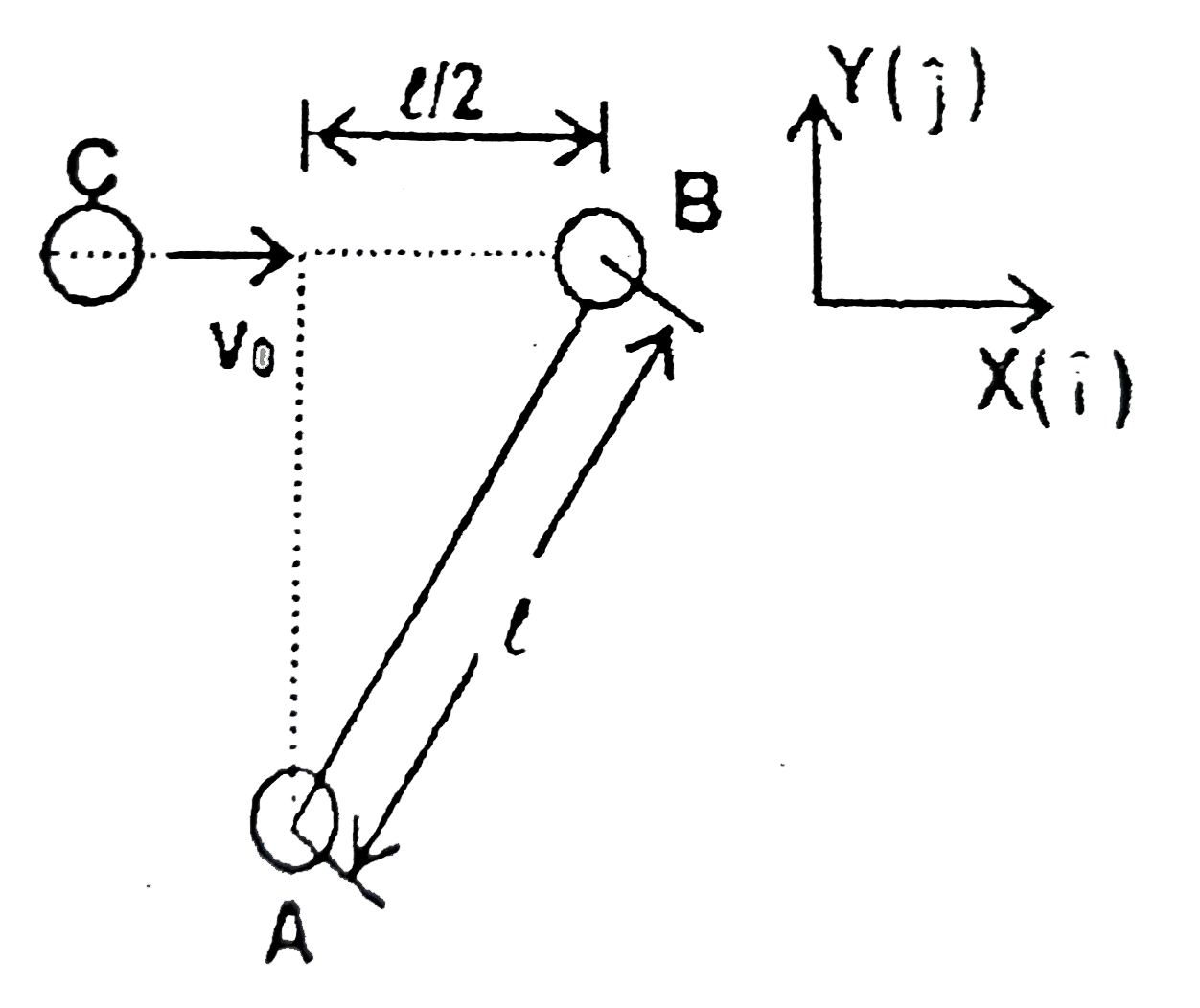
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Three spheres, each of mass m, can slide freely on a frictionless, hor...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of mass m slides with velocity v on as frictionless surface t...
Text Solution
|
- Three spheres, each of mass m , can slide freely on a frictionless, ho...
Text Solution
|
- Three spheres, each of mass m, can slide freely on a frictionless, hor...
Text Solution
|
- Three spheres, each of mass m, can slide freely on a frictionless, hor...
Text Solution
|
- Three spheres, each of mass m, can slide freely on a frictionless, hor...
Text Solution
|
- Two equal spheres B and C , each of mass m , are in contact on a smoot...
Text Solution
|
- The sphere A of mass m(1) moves with velocity V on a frictionless hori...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere A of mass m moving with a velocity hits another stationary sp...
Text Solution
|