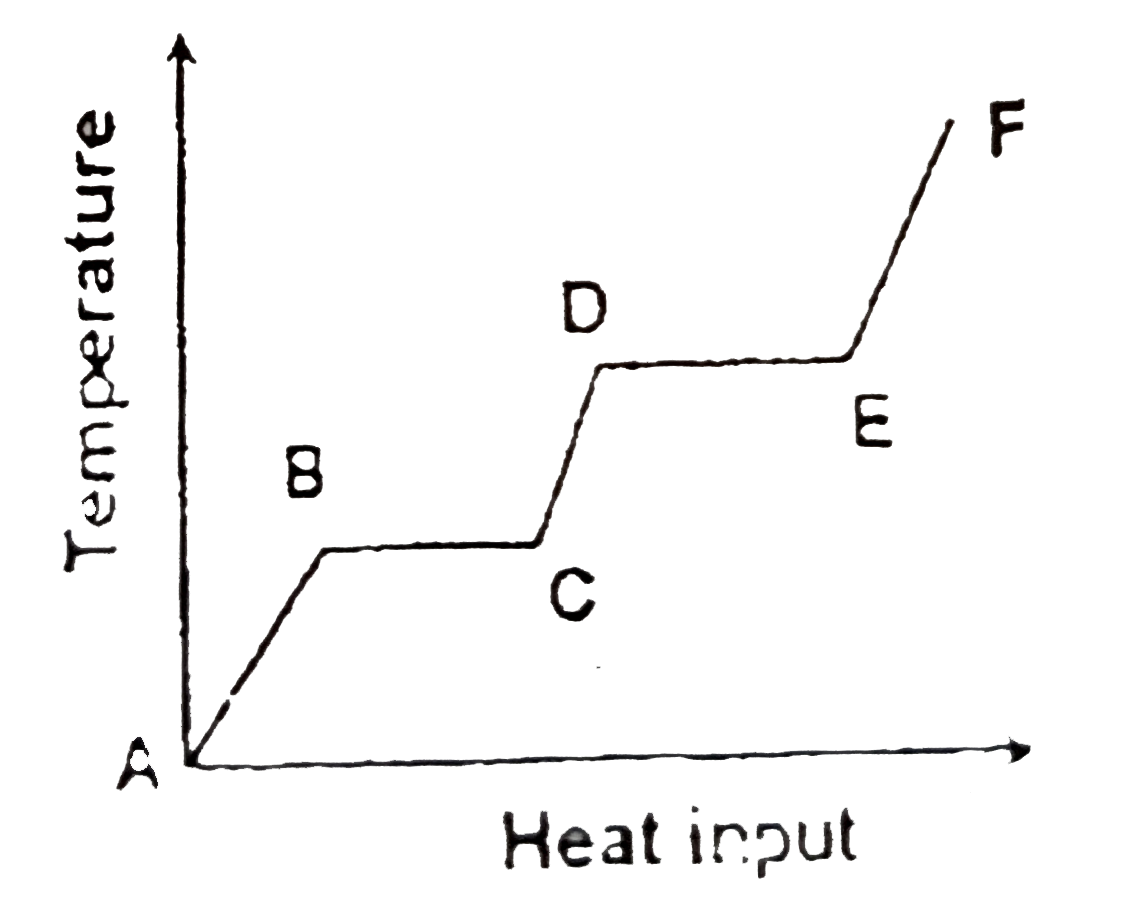
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- When we raise the temperature of a body, the molecules and atoms move ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid material is supplied heat at a constant rate. The temperature...
Text Solution
|
- During heat exchange, temperature of a solid mass does not change. In ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid material is supplied with heat at a constant rate. The tempera...
Text Solution
|
- In spite of supplying heat, the temperature of the melting solid does ...
Text Solution
|
- A source of heat supplies heat at constant rate to a solid cube. The v...
Text Solution
|
- A solid material is provided with heat at a fixed rate and the tempera...
Text Solution
|
- एक ठोस पदार्थ को नियत दर से ऊष्मा दी जाती है । पदार्थ का ताप दी गई ऊष्...
Text Solution
|
- A source of heat supplies heat at a constant rate to solid cube. The ...
Text Solution
|