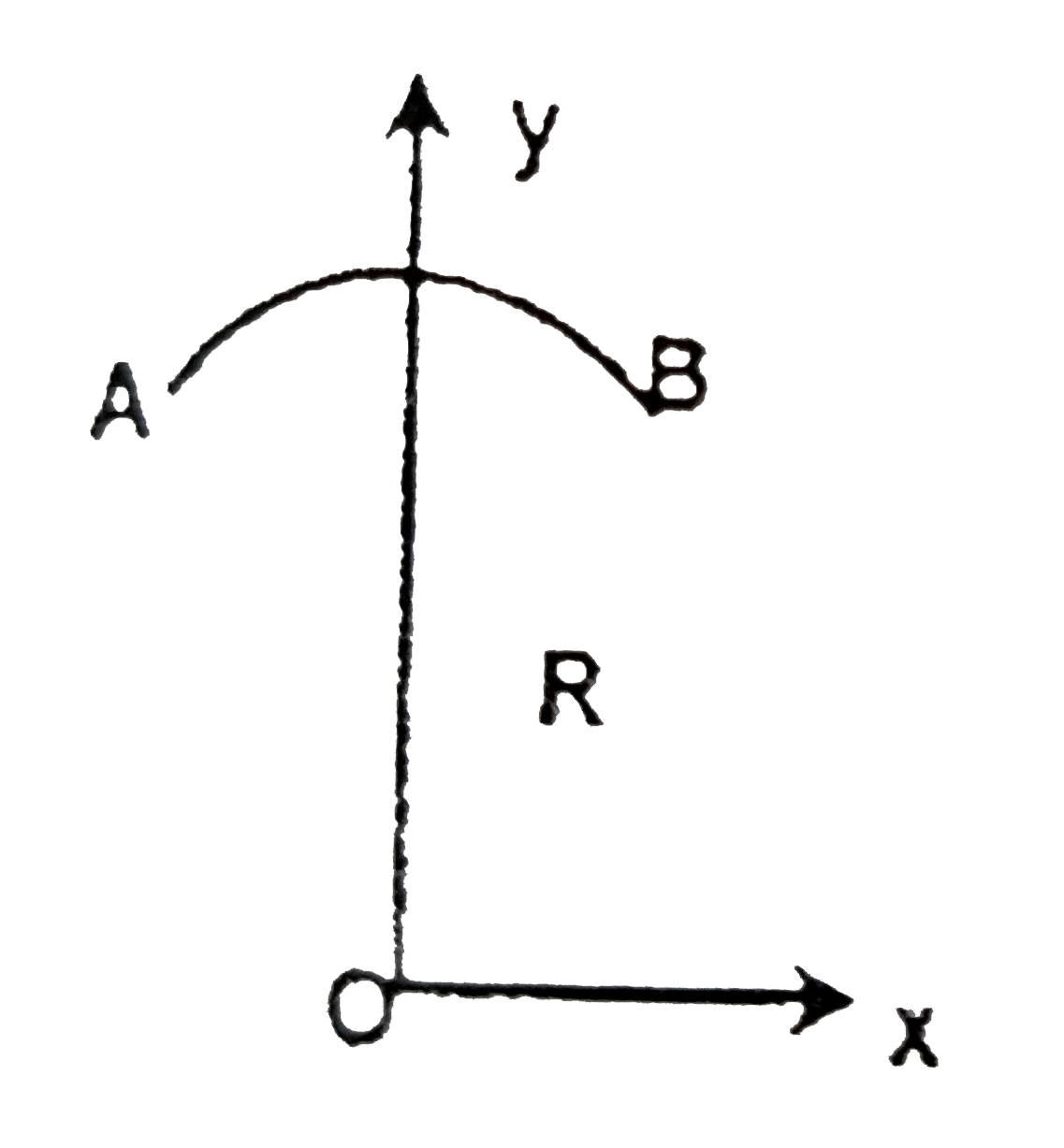
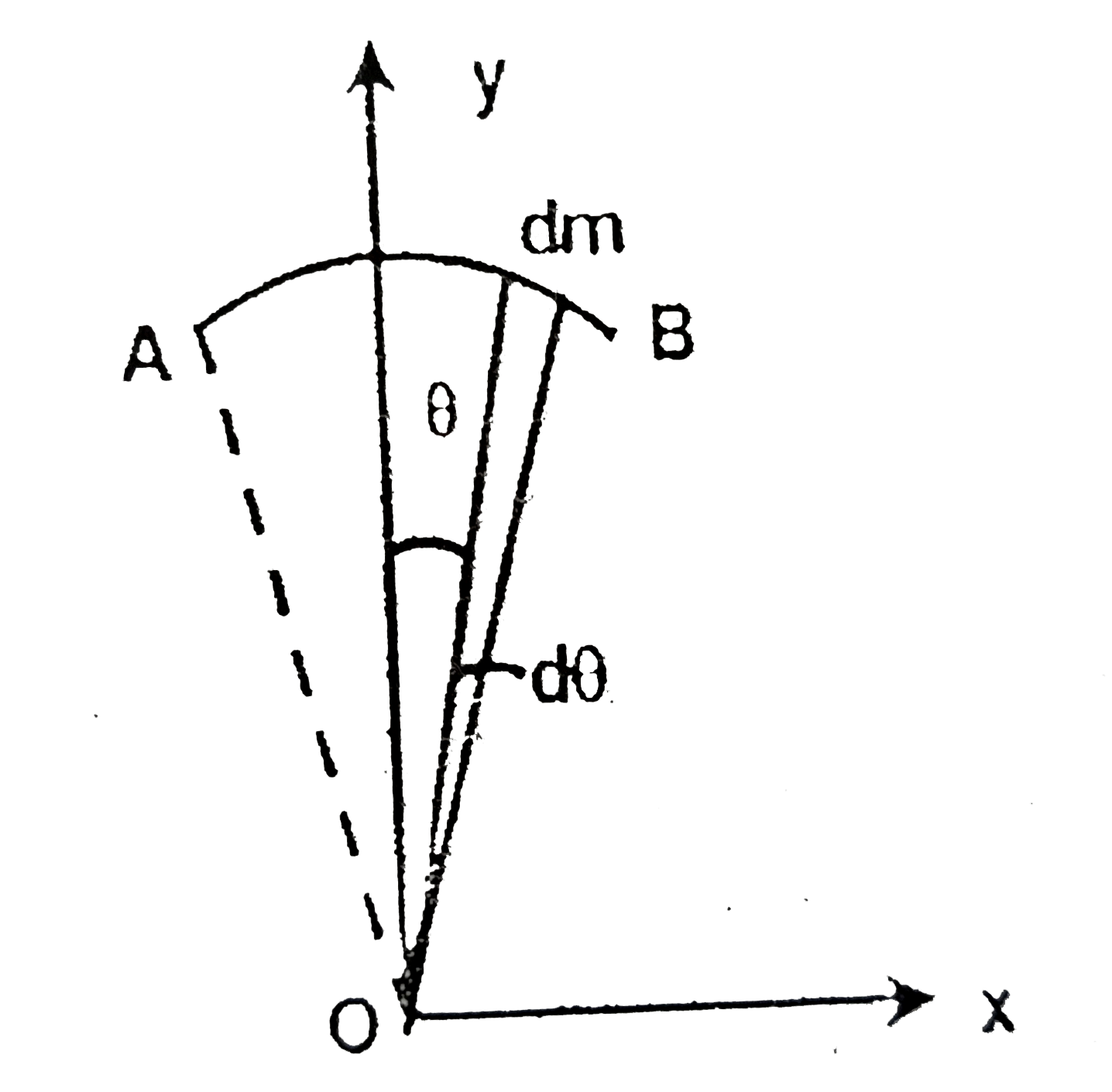
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FIITJEE-CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM-Example
- A carpet of unit mass an unit length is laid on the floor. One end of ...
Text Solution
|
- PQR is a wedge fixed to the floor. Two blocks A & B of equal mass m=1k...
Text Solution
|
- An elastic ball of mass 'm' is suspended from a fixed point by an inex...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is projected from a point in a horizontal plane so as to strike...
Text Solution
|
- A tiny ball of mass m is released from the state of rest over a large ...
Text Solution
|
- A point objects of mass m is slipping down on a smooth hemispherical b...
Text Solution
|
- An iron ball of mass m, suspended by a light inextensible string of le...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is released from height ‘h’ on smooth quarter cir...
Text Solution
|
- A ping-pong ball of mass m is floating in air by a jet of water emergi...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is pushed towards a movable wedge of mass 2 m and he...
Text Solution
|
- A circular are (AB) of thin wire frame of radius R and mass M makes an...
Text Solution
|
- From a 16cmxx8cm rectangular uniform plane sheet, exactly one quarter ...
Text Solution
|
- A block B is at rest on the rough horizontal surface as shown. Another...
Text Solution
|
- An infinite number of bricks are placed one over the other as shown in...
Text Solution
|
- A particle strikes a smooth horizontal surface at an angle of 45^(@) w...
Text Solution
|