Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FIITJEE-FLUID MECHANICS-Example
- A horizontally oriented bent thin tube ABC of length 1.4 m rotates wit...
Text Solution
|
- Two soap bubbles are stuck together with an intermediate film separati...
Text Solution
|
- A long cylindrical tank of cross-sectional area 0.5m^(2) is filled wit...
Text Solution
|
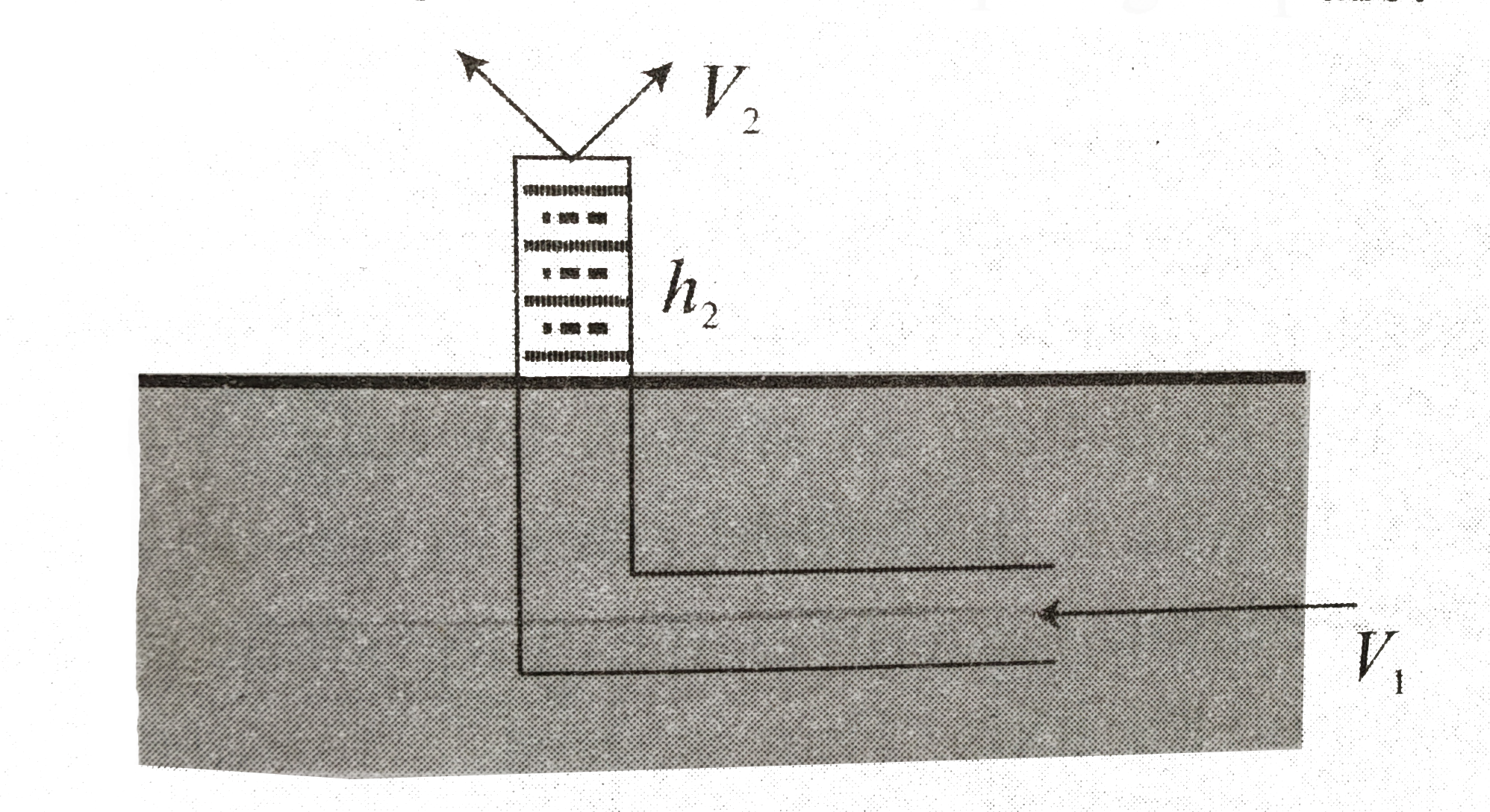
- A bent tube is lowered into a water stream as shown in figure. The vel...
Text Solution
|
- A pipe of diameter D is connected to a water tank of large cross-secti...
Text Solution
|
- A light cylindrical vessel is kept on a horizontal surface it's base a...
Text Solution
|
- The density of ice is xgm//c c and that of water is y gm//c c. What is...
Text Solution
|
- A cube of mass m and density D is suspended from a point P by a spring...
Text Solution
|
- Eight identical droplets, each falling under gravity in the earth's at...
Text Solution
|
- Water rises to a height of 10cm in a certain capillary tube. An anothe...
Text Solution
|
- An air bubble of radius 5mm rises through a vat of syrup at a steady s...
Text Solution
|
- n number of water droplets, each of radius r, coalese, to form a singl...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical ball of radius 1 cm and density 4 xx 10^3 kg is dropped ge...
Text Solution
|
- For a stream line flow of water following statements are given below ...
Text Solution
|
- Buoyant force on an object completely immersed in a fluid does not dep...
Text Solution
|