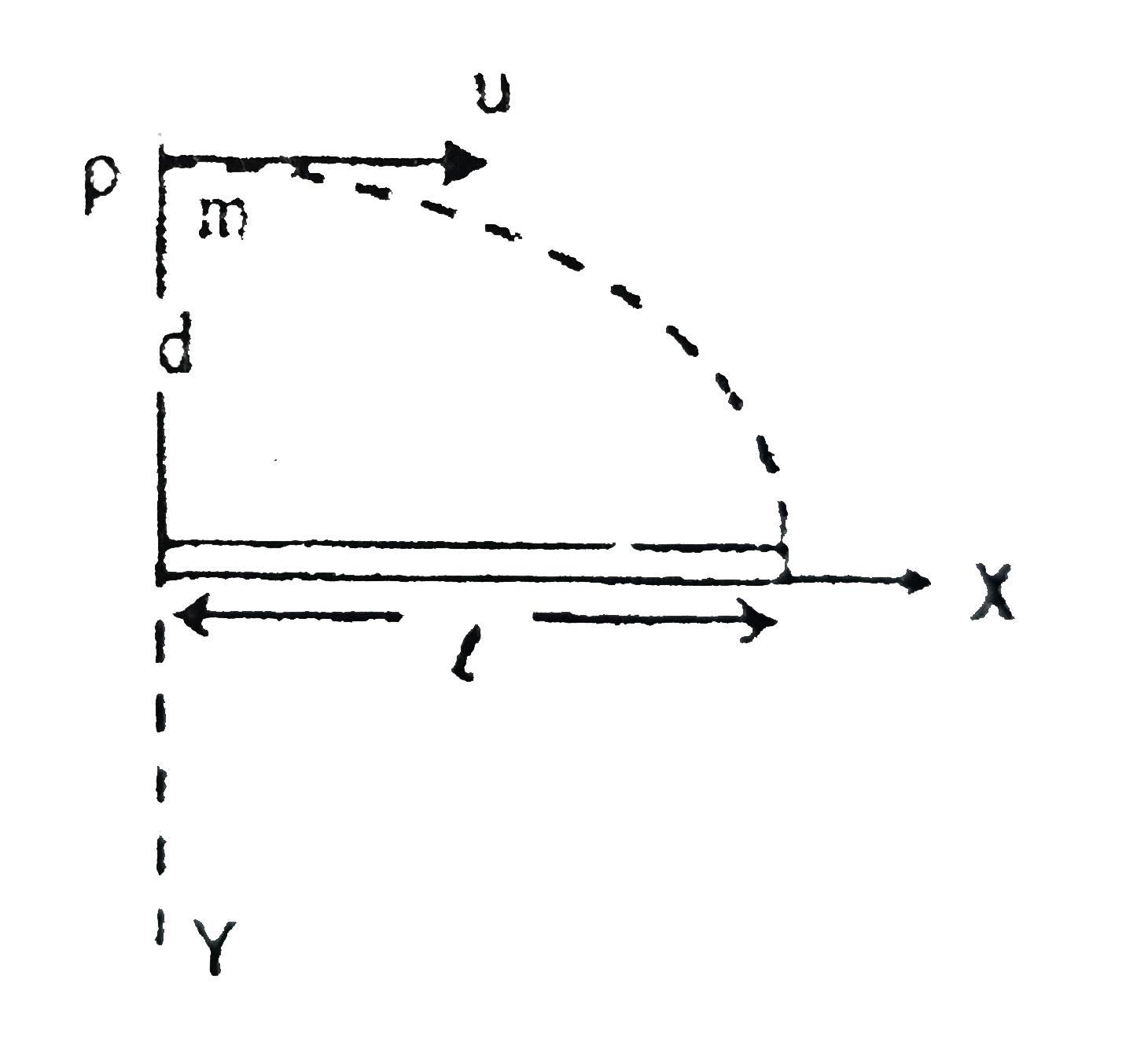
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- An electron is projected from a distance d and with initial velocity u...
Text Solution
|
- An electron is projected as shown in fig. with kinetic energy K, at an...
Text Solution
|
- An electric field E is produced between two parallel plates having a s...
Text Solution
|
- The plates of small size of a parallel plate capacitor are charged as ...
Text Solution
|
- An electron is projected as shown with speed u . If electron just fail...
Text Solution
|
- An electron (charge = e, mass = m) is projected horizontally into a un...
Text Solution
|
- Into the region of space between the plates of a parallel-plate capaci...
Text Solution
|
- Three charged conducting plates are separated by small distances as sh...
Text Solution
|
- An electron is projected from a distance d and with initial velocity u...
Text Solution
|