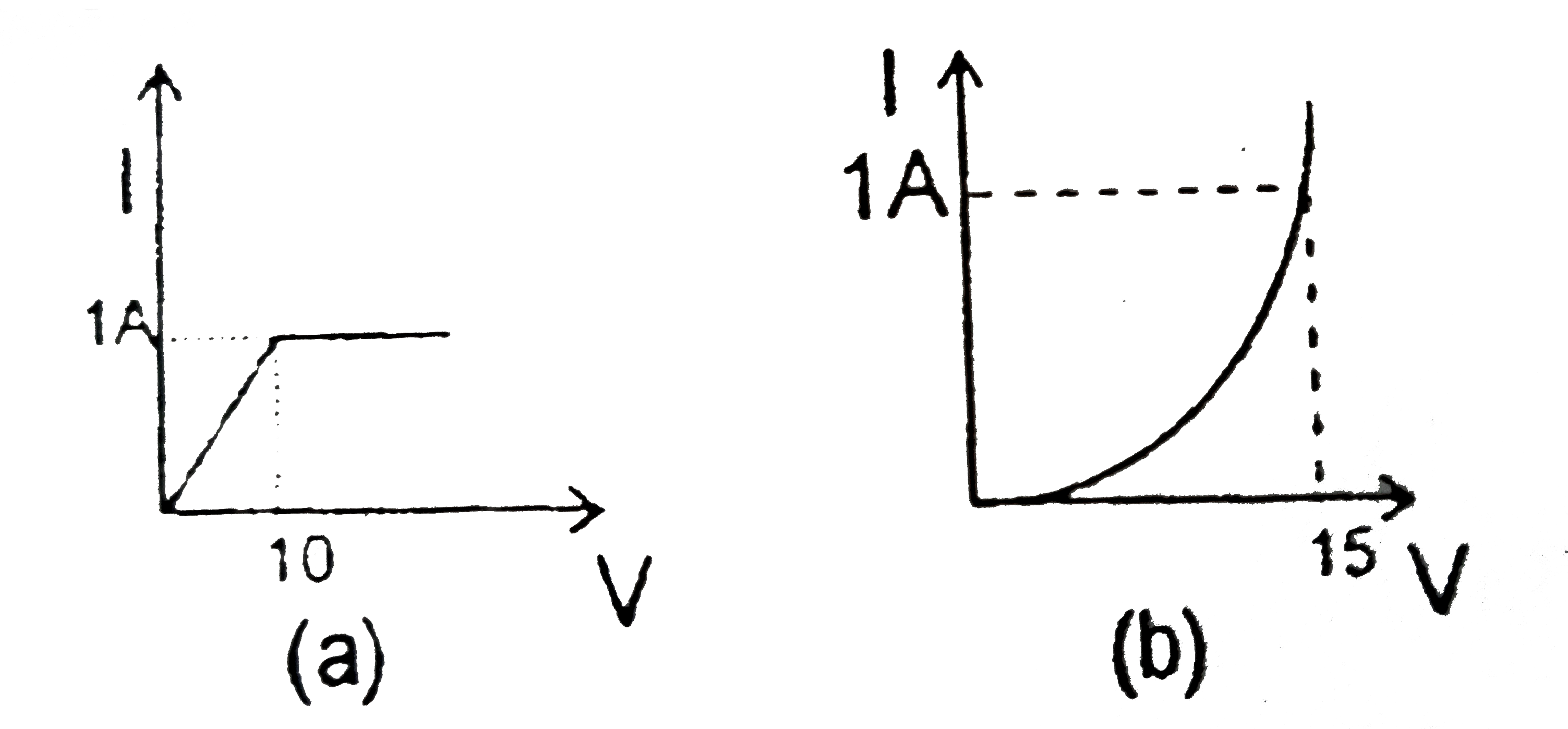
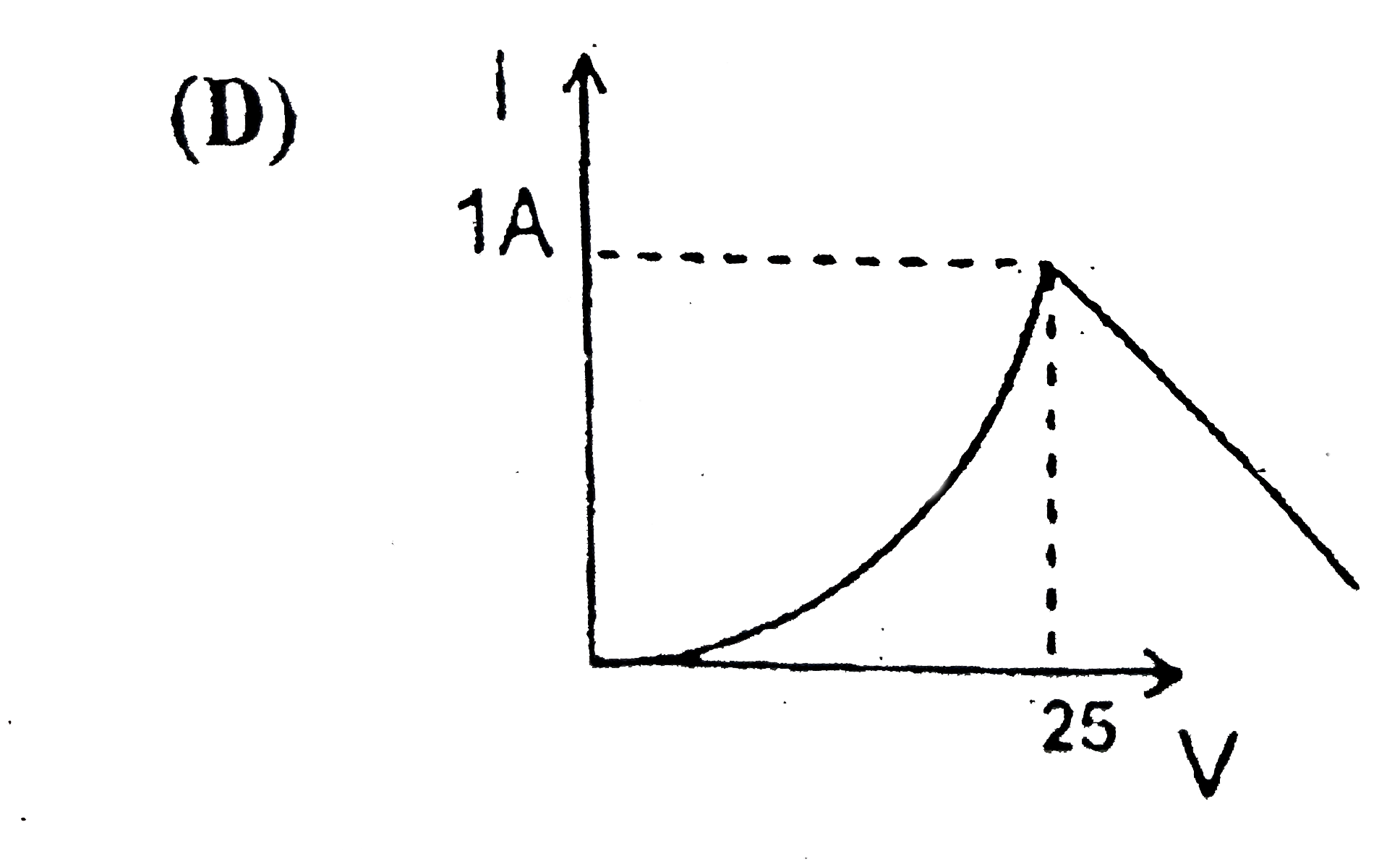A
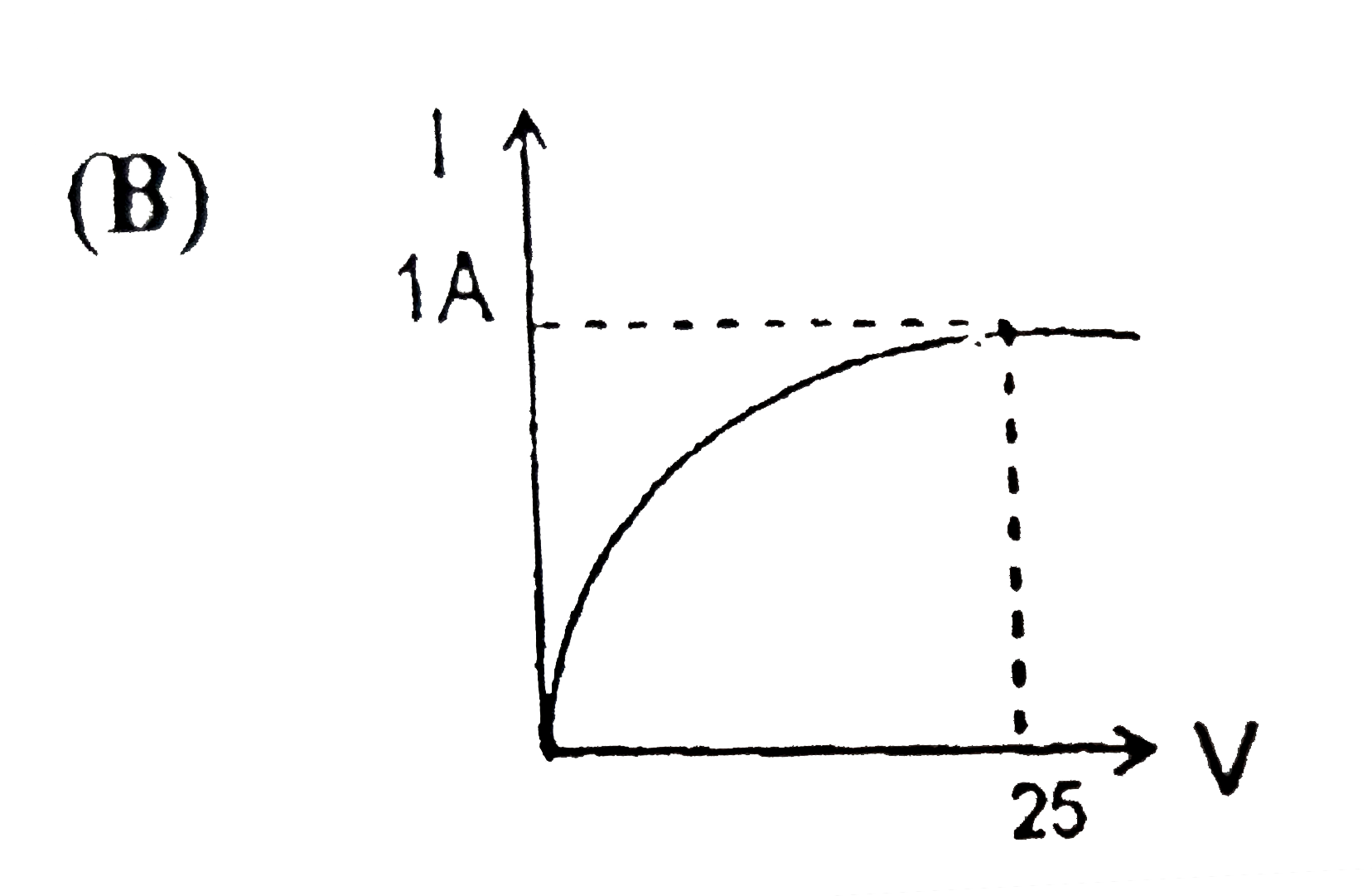
B
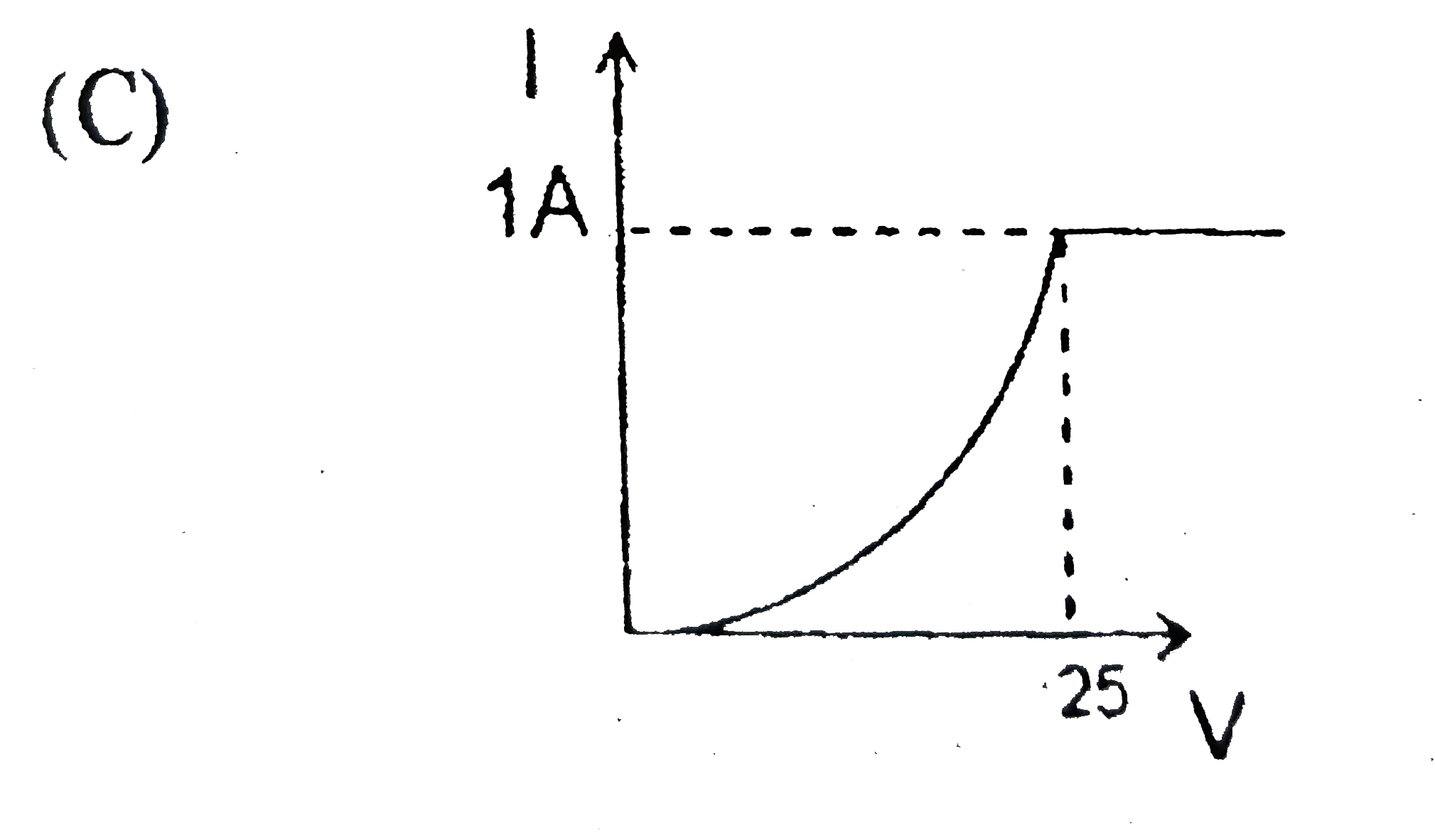
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Current-voltage characteristics of two elements A and B are as shown i...
Text Solution
|
- The voltage-current graphs for two resistor of the same meterial and t...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a box with three terminals on top of it as shown in figure. ...
Text Solution
|
- The graph shown in Fig. represents the I-V characteristics of a zener ...
Text Solution
|
- Current-voltage characteristics of two elements A and B are as shown b...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the voltage current characteristic fo a zener diode.
Text Solution
|
- Draw the voltage-current charateristics of a p-n junction and compare ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following represents the value of voltage and current at ...
Text Solution
|
- The following graphs represent the current versus voltage and voltage ...
Text Solution
|