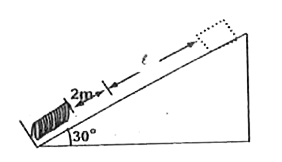
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- An ideal massless spring S can compressed 1.0 m in equilibrium by a fo...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 2.0 kg is moving on a frictionless horizontal surface ...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal massless spring S can compressed 1.0 m in equilibrium by a fo...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal massless spring S can compressed 1.0 m in equilibrium by a fo...
Text Solution
|
- A block of 4kg mass starts at rest and slides a distance d down a fric...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 4 kg slides on a horizontal frictionless surface with ...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 0.1 g moving with a velocity of 10 m/s hits a spring (f...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal massless spring is compressed by 1 m by a force of 100 N. The...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal massles spring S can be compressed 1 m by a force of 100 N in...
Text Solution
|
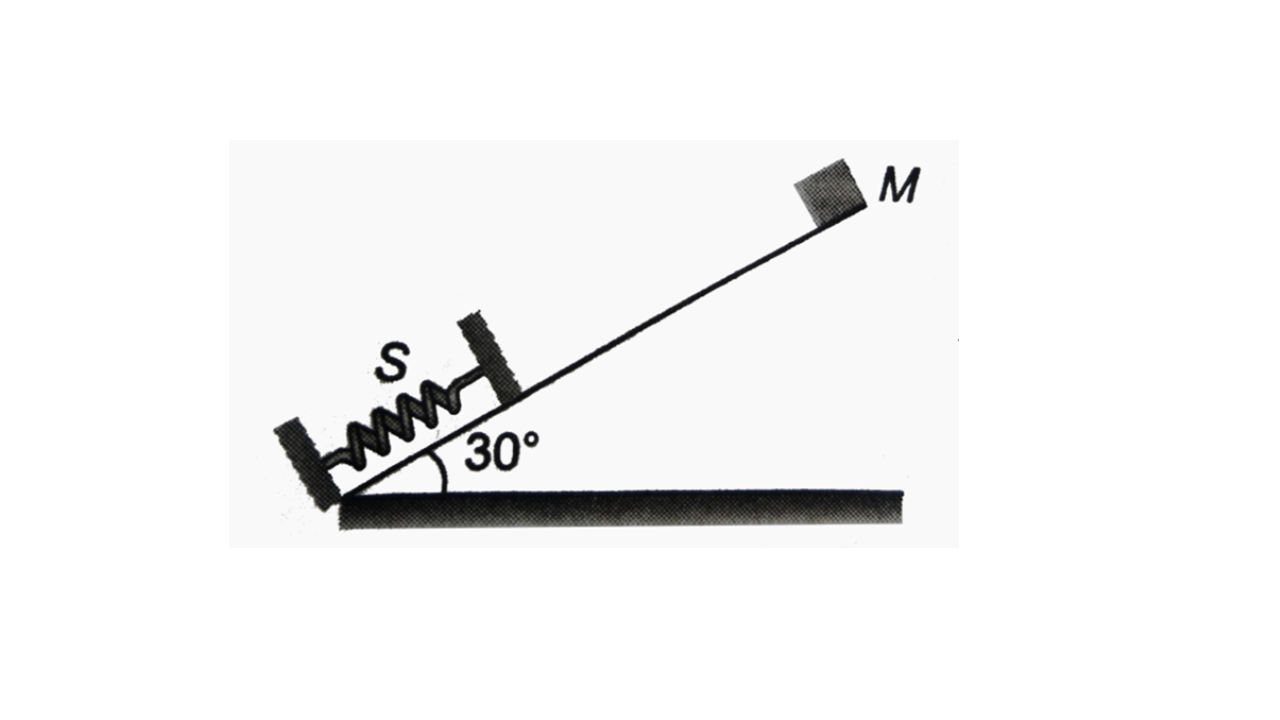 .
.