Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
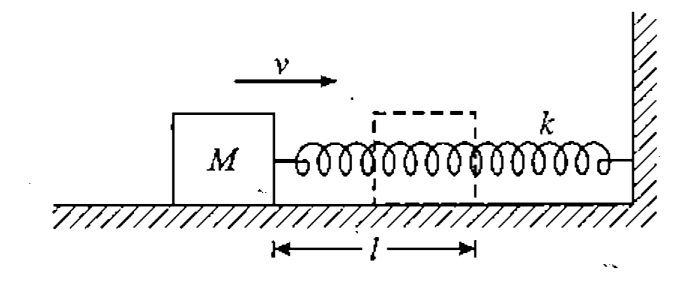
- The block of mass M in figure -4.160, initially has a velocity v(o) to...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown masses of the blocks A, B and C are 6kg, 2kg and 1...
Text Solution
|
- A block with mass 0.50 kg is forced against a horizontal spring of neg...
Text Solution
|
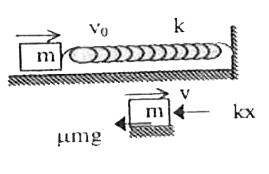
- A block of mass m is moving with a speed v on a horizontal rough surfa...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is attached to two unstretched springs of spring con...
Text Solution
|
- Block of mass 2 m is given v(0) towards the right. If L is the natural...
Text Solution
|
- Two springs are in a series combination and are attached to a block of...
Text Solution
|
- Two block of same mass'm' are joined with an dideal spring of spring c...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 2.0 kg is given an initial speed along the floor towar...
Text Solution
|