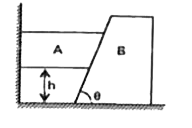
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Two smooth wedges of equal mass m are placed as shown in figure. All s...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in figure, the rod of mass mhelp by two smoot...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown A and B are free to move . All the surface are smo...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in figure, the rod of mass m held by two smoo...
Text Solution
|
- All surfaces shown in figure are smooth. Wedges of mass 'M' is free to...
Text Solution
|
- Wedges B and C are smooth and they are placed in contact as shown. Blo...
Text Solution
|
- In the Fig. shown, mass 'm' is being pulled on the incline of a wedge ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is placed at rest on the top of a smooth wedge of...
Text Solution
|
- All the surfaces are smooth as shown in figure. The acceleration of ma...
Text Solution
|