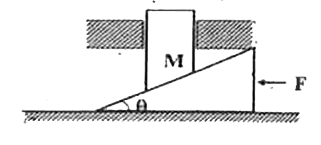
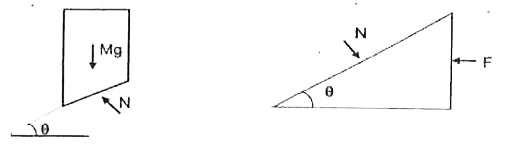
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- What is the power required to push the woodn wedge horizontally with c...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a small block of mass m which is started with a speed v o...
Text Solution
|
- A system of wedge and block as shown in figure, is released with the s...
Text Solution
|
- All surfaces shown in figure are smooth. Wedges of mass 'M' is free to...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on the inclined sufrace of a wedge as show...
Text Solution
|
- In figuer, shown all the surfaces are frictionless, and mass of the bl...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is pushed towards the movable wedge of mass M and he...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m rests on a wedge of mass M which, in trun, rests on ...
Text Solution
|
- For the figure shown, block of mass m is released from the rest. Find ...
Text Solution
|