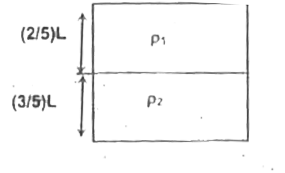
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A cube of 1 kg is floating at the interface of two liquids of densi...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic sphere floats in an immiscible mixture of water (rho(w)=10^...
Text Solution
|
- A block of material has a density rho(1) and floats three-fourth subme...
Text Solution
|
- The light cone is in equilibrium under the action of hydrostatic force...
Text Solution
|
- Two substances of densities rho(1) and rho(2) are mixed in equal volum...
Text Solution
|
- A jar filled with two non-mixing liquid 1 and 2 having densities rho(1...
Text Solution
|
- एक बेलनाकार ब्लॉक एक बर्तन में लिये गये घनत्व rho(1) के द्रव में ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform sphere of density rho floats at the interface of two liquids...
Text Solution
|
- A block of density rho(1) floats in two immiscible liquids of density ...
Text Solution
|