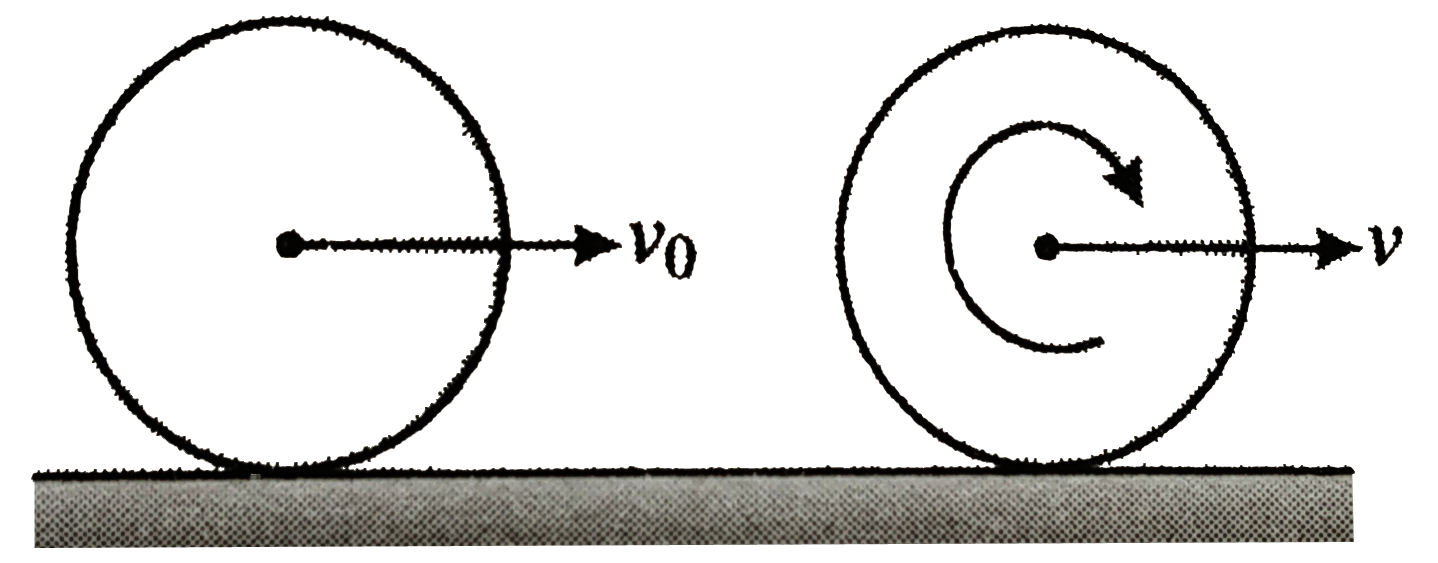Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A uniform disc of mass m and radius r is projected horizontally with v...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform ring of radius R is given a back spin of angular velocity V(...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disk of mass m and radius R is projected horizontally with v...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass m and radius R is projected horizontally with v...
Text Solution
|
- A small body of mass m is at rest inside a narrow groove carved in a d...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass m and radius R is projected horizontally with v...
Text Solution
|
- A ring of mass m and radius R is placed on a rough horizontal surface ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc having mass m and radius R v(0) A rod is projected on a...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform ring of mass 'm' and radius 'R' is projected horizontally wi...
Text Solution
|