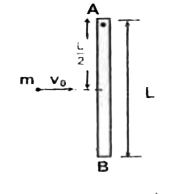
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A uniform rod AB which is free to swing in the vertical plane about a ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of mass M and length a lies on a smooth horizontal plane...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod AB of length 2l and mass m is rotating in a horizontal p...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod AB of length l and mass m hangs from point A in a car mo...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod is resting freely over a smooth horizontal plane. A part...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of length L lies on a smooth horizontal table. The rod h...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod AB of length L and mass M is lying on a smooth table. A ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of mass M and length L lies on a frictionless horizontal...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of length lambda lies on a smooth horizontal table A par...
Text Solution
|