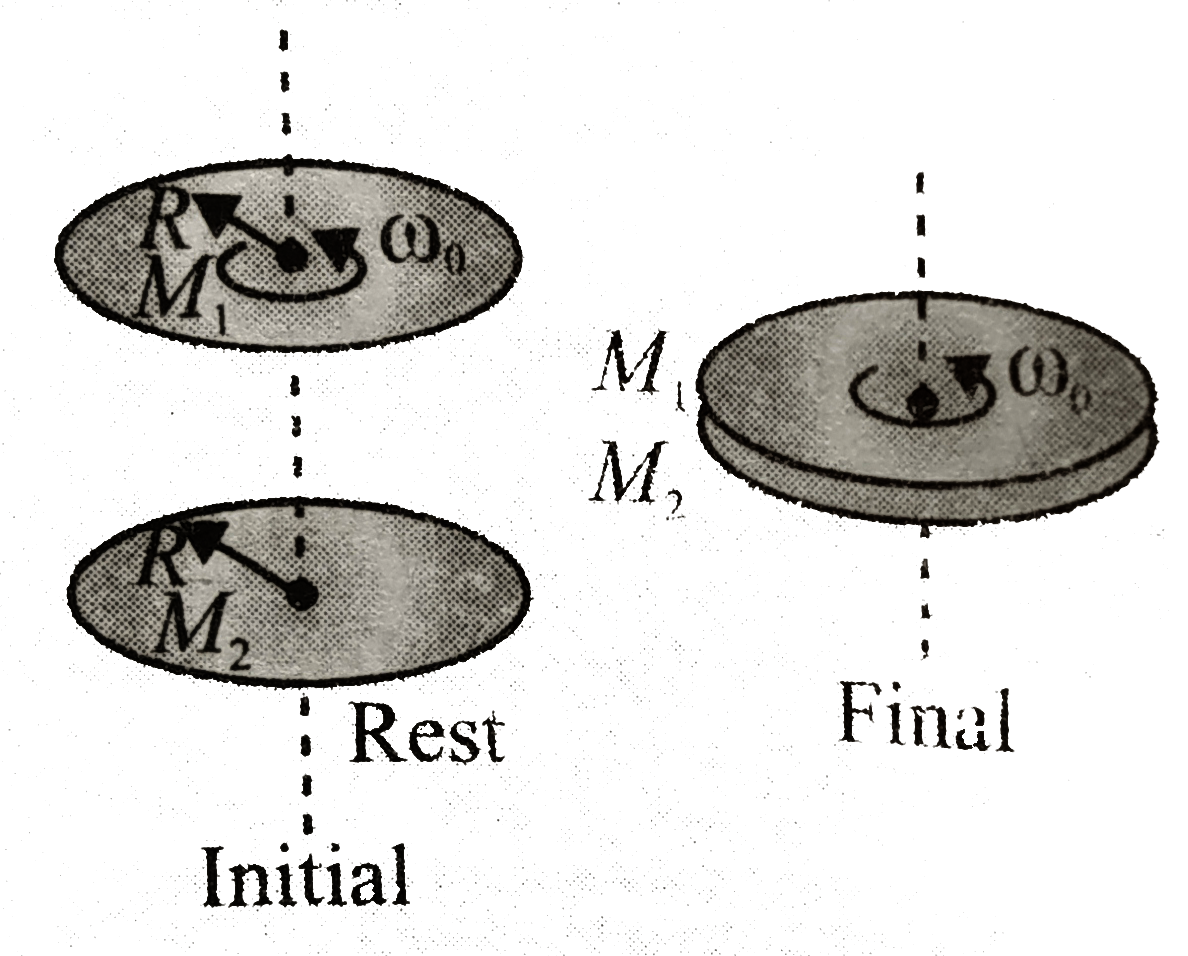A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A circular disc of mass M(1) and radius R, initially moving, With a co...
Text Solution
|
- A circular disc of mass M(1) and radius R , initially moving, With a c...
Text Solution
|
- Initial angular velocity of a circular disc of mass M is omega(1) . Th...
Text Solution
|
- A circular disc is rotating without friction about its natural axis wi...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform circular disc of mass M and radius R is rotating in a h...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of mass m and radius r is gently placed on another disc of mass...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass M and radius R is rotating in a horizontal plan...
Text Solution
|
- A circular disc of mass M and radius R is rotating with angular veloci...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of mass M and radius R is rolling with angular speed w on horiz...
Text Solution
|