A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A reaction is spontaneous if free energy change Delta G for the reacti...
Text Solution
|
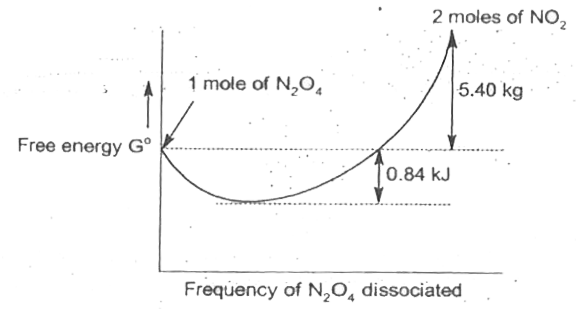
- Gaseous N2O4 dissociates into gaseous NO2 according to the reaction N2...
Text Solution
|
- The reaction which is in dynamic equilibrium, ensured us, that the rea...
Text Solution
|
- Delta G is energy availabe to do useful work and is thus a meaure of "...
Text Solution
|
- (A) An electrochemical cell can be set-up only if the redox reaction i...
Text Solution
|
- N2O4(g) hArr 2NO2(g) . In this reaction, NO2 is 20% of the total volum...
Text Solution
|
- A reaction is spontaneous if free energy change DeltaG , for the react...
Text Solution
|
- For the following reaction at equilibrium 2NO2(g) harr N2O4(g) Delta...
Text Solution
|
- For spontaneous reaction ,the change in free energy should be…
Text Solution
|