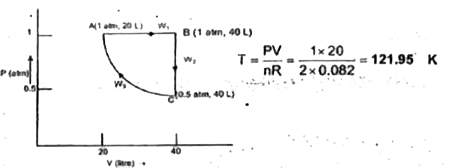
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Two moles of a perfect gas undergo the following processes: a. A rev...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of a perfect gas undergo the following processes: a. A rev...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of a perfect gas undergo the following process: (a) A revers...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of an ideal gas undergo the following process : (a) a reve...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a non-ideal gas undergoes a change of state (1.0 atm,3.0 ...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas undergoes a change of state (2.0) atm, 3.0 L)...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of a perfect gas undergo the following processes: (a) a reve...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of a perfect gas undergo the following processes: a. A rev...
Text Solution
|
- A quantity of an ideal gas at 20^(@)C reversibly expands against a con...
Text Solution
|