A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Consider following figure and answer the questions at the end of it. F...
Text Solution
|
- A complex of iron and cyanide ions is 100% ionised ar 1 m (molal). If ...
Text Solution
|
- A complex iron and cyanide ions is 100% ionised at 1 m (molal) . I...
Text Solution
|
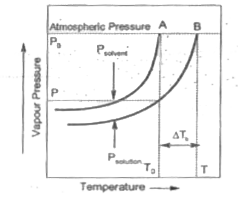
- Figure explains elevation in boiling point when a non-volatile solute ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure explains elevation in boiling point when a non-volatile solute ...
Text Solution
|
- क्वथनांक एवं क्वथनांक में उन्नयन को परिभाषित कीजिए । किसी द्रव में अवा...
Text Solution
|
- One molal solution of a complex of cobalt chloride with NH(3) in water...
Text Solution
|
- Consider following figure and answer the questions at the end of it. F...
Text Solution
|
- Consider following figure and answer the questions at the end of it. F...
Text Solution
|