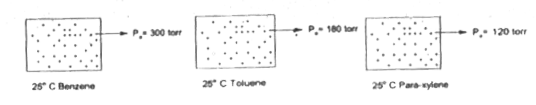
If benzene. Toluene and para-xylene are mixed in molar ratio 1:2:3.
Then answer the following question carefully.
Estimate the dew point pressure (At the dew point pressure all liquid vaporiaed ) for the above mixture (approximately)

If benzene. Toluene and para-xylene are mixed in molar ratio 1:2:3.
Then answer the following question carefully.
Estimate the dew point pressure (At the dew point pressure all liquid vaporiaed ) for the above mixture (approximately)
A
180 torr
B
152 torr
C
138 torr
D
156 torr
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
B
At the dew point pressure all liquid vaporized
`(1)/(P_(("dew point")))=[(Y_(B))/(P_(B)^(@))+(y_(T))/(P_(T)^(@))+(Y_(X))/(P_(X)^(@))]" " (Y_(B)=(1)/(6), Y_(T)=(2)/(6), Y_(X)=(3)/(6))`
`(1)/(P_(("dew point")))=[(Y_(B))/(P_(B)^(@))+(y_(T))/(P_(T)^(@))+(Y_(X))/(P_(X)^(@))]" " (Y_(B)=(1)/(6), Y_(T)=(2)/(6), Y_(X)=(3)/(6))`
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
If benzene. Toluene and para-xylene are mixed in molar ratio 1:2:3. Then answer the following question carefully. Estimate the bubble point pressure (At the bubble point pressure all liquid exist. No trace of vapour in mixture) for the above mixture.
Two liquids X and Y form an ideal solution. The mixture has a vapour pressure of 400 mm at 300 K when mixed in the molar ratio 1:1. when mixed in the molar ratio of 1:2 at the same temperatre the vapour pressure of the mixture is 350 mm. The vapour pressure of the two pure liquids X and Y respectively are
Two liquids having vapour pressure P_1^0 and P_2^0 in pure state in the ratio of 2:1 are mixed in the molar ratio 1:2 The ratio of their moles in the vapour state would be
A point charge q_1 is placed inside cavity 1 and another point charge q_2 is inside cavity 2. A point charge q is placed outside the conductor. For the situation described above, answer the following questions. If charge q_2 is at point Q (inside cavity 2), then vecE at the center of cavity 2 due to induced charge on the surface of cavity 2 would be
A point charge q_1 is placed inside cavity 1 and another point charge q_2 is inside cavity 2. A point charge q is placed outside the conductor. For the situation described above, answer the following questions. vecE inside the conductor at point S distant r from point charge q, due to charge on outer surface of the conductor, would be
In the study of titration of NaOH and Na_(2)CO_(3) . NaOH and NaHCO_(3) , Na_(2)CO_(3) and NaHCO_(3) , phenophthalein and methyl orange are used as indicators. (a). When phenolphthalein is used as an indicator for the above mixture: (i). It indicates complete neutralisation of NaOH or KOH (ii). It indicates half neutralisation of Na_(2)CO_(3) because NaHCO_(3) is formed at the end point. (b). When methyl orange is used as an indicator for the above mixture (i). It indicates complete neutralisation of NaOH or KOH (ii). It indicates half neutralisation of Na_(2)CO_(3) because NaCl is formed at the end point. Q. 1 L solution of Na_(2)CO_(3) and NaOH was made in H_(2)O . 100 " mL of " this solution required 20 " mL of " 0.4 M HCl in the presence of phenolphthalein however, another 100 mL sample of the same solution required 25 " mL of " the same acid in the presence of methyl orange as indicator. What is the molar ratio of Na_(2)CO_(3) and NaOH in the original mixture.
When NO and NO_(2) are mixed, the following equilibria are readily obtained, 2NO_(2) hArr N_(2)O_(4), K_(p)=6.8 atm^(-1) NO+NO_(2) hArr N_(2)O_(3) In an experiment when NO and NO_(2) are mixed in the ratio of 1:2 , the final total pressure was 5.05 atm and the partial pressure of N_(2)O_(4) was 1.7 atm. Calculate a. the equilibrium partial pressure of NO . b. K_(p) for NO+NO_(2) hArr N_(2)O_(3) .
A liquid having density 6000 kg//m^(3) stands to a height of 4 m in a sealed tank as shown in the figure. The tank contains compressed air at a gauge pressure of 3 atm . The horizontal outlet pipe has a cross-sectional area of 6 cm^(2) and 3 cm^(2) at larger and smaller sections. Atmospheric pressure = 1 atm, g = 10m//s^(2) 1 atm =10^(5) N//m^(2) . Assume that depth of water in the tank remains constant due to s very large base and air pressure above it remains constant. Based on the above information, answer the following questions. The height at which liquid will stand in the open end of the pipe is
A point charge q_1 is placed inside cavity 1 and another point charge q_2 is inside cavity 2. A point charge q is placed outside the conductor. For the situation described above, answer the following questions. If the potential of the conductor is V_0 and charge q_2 is placed at the center of cavity 2, then potential at point Q is
Properties such as boiling point, freezing point and vapour pressure of a pure solvent change when solute molecules are added to get homogeneous solution. These are called colligative properties. Applications of colligative properties are very useful in day-to-day life. one of its examples is the use of ethylene glycol adn water mixtures as anti-freezing liquid in the radiator of automobiles. A solution M is prepared by mixing ethanol and water. The mole fraction of ethanol in the mixture is 0.9 . Given: Freezing point depression constant of water (K_(f)^(water)) = 1.86 K kg mol^(-1) Freezing point depression constant of ethanol (K_(f)^("ethanol")) = 2.0 K kg mol^(-1) Boiling point elevation constant of water (K_(b)^(water)) = 0.52 K kg mol^(-1) Boiling point elevation constant of ethanol (K_(b)^("ethanol")) = 1.2 K kg mol^(-1) Standard freezing point of water = 273 K Standard freezing point of ethanol = 155.7 K Standard boiling point of water = 373 K Standard boiling point of ethanol = 351.5 K Vapour pressure of pure water = 32.8 mm Hg Vapour pressure of pure ethanol = 40 mm Hg Molecular weight of water =18 g mol^(-1) Molecular weight of ethanol = 46 g mol^(-1) In answering the following questions, consider the solutions to be ideal dilute solutions and solutes to be non-volatile and non-dissociative. The freezing point of the solution M is
Recommended Questions
- If benzene. Toluene and para-xylene are mixed in molar ratio 1:2:3. ...
Text Solution
|
- Define dew point temperature.
Text Solution
|
- What is dew point temperature ? OR Define dew point temperature ?
Text Solution
|
- What is dew point temperature?
Text Solution
|
- What is the dew point temperature ?
Text Solution
|
- If benzene. Toluene and para-xylene are mixed in molar ratio 1:2:3. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A tin contains a mixture of Dew and Sprite in the ratio of 7:3 and ano...
Text Solution
|
- If benzene toluene and para-xylene are mixed in molar ratio 1 : 2: 3. ...
Text Solution
|
- If benzene toluene and para-xylene are mixed in molar ratio 1 : 2: 3. ...
Text Solution
|