A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
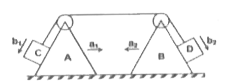
- Let vec( a) (1) and vec( a) (2) are the acceleration of wedges A and B...
Text Solution
|
- Let vec a , vec ba n d vec c be pairwise mutually perpendicular v...
Text Solution
|
- Let vec a , vec b , vec c be three unit vectors such that | vec a+ v...
Text Solution
|
- Let |vec a| = |vec b| = |vec a-vec b| = 1. Then the angle between vec ...
Text Solution
|
- Let | vec a | = | vec b | = 2 and | vec c | = 1 Also (vec a-vec c) * (...
Text Solution
|
- Let vec(a), vec(b), vec(c) be vectors of length 3, 4, 5 respectively. ...
Text Solution
|
- Let vec(a),vec(b),vec (c ) be the positions vectors of the vertices of...
Text Solution
|
- Let vec(a) , vec(b),vec(c) be vectors of length 3,4,5 respectively. Le...
Text Solution
|
- Let vec a , vec ba n d vec c be pairwise mutually perpendicular v...
Text Solution
|