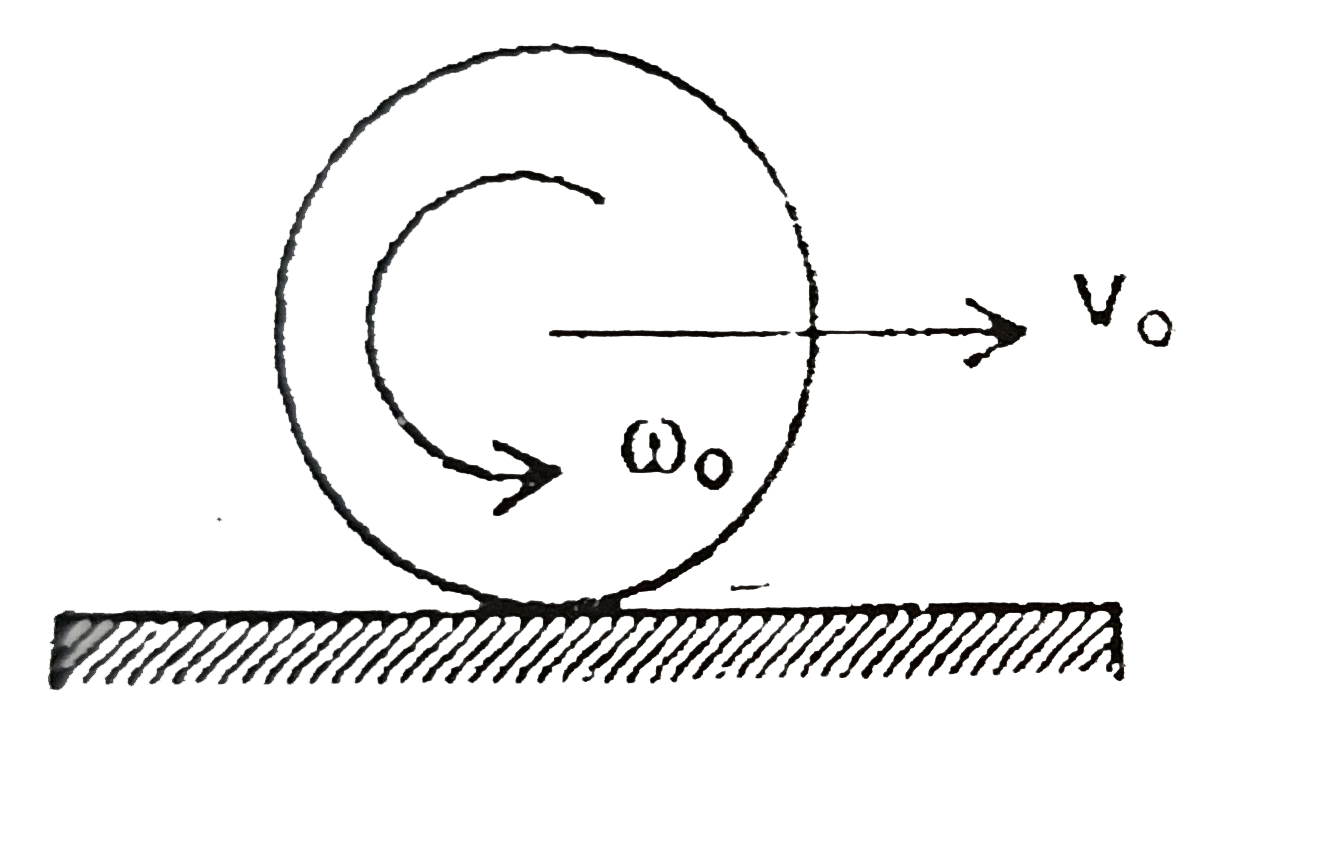Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A disc of radius R is spun to an angular speed omega(0) about its axis...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius R and mass m is projected on to a horizontal floor wi...
Text Solution
|
- A disc roating about its axis with angular speed omega(0) is placed li...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform circular disc of radius r . 1placed on a rough horizontal pl...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius R is spum to an angular speed omega about its axis an...
Text Solution
|
- A disc is given an angular velocity omega(0) and a linear velocity v(0...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of mass m and radius r is gently placed on another disc of mass...
Text Solution
|
- अपने अक्ष पर omega(0) कोणीय चाल से घूर्णन करने वाली किसी चक्रिका को धी...
Text Solution
|
- A disc rotating about its axis with angular speed omega(0) is placed l...
Text Solution
|