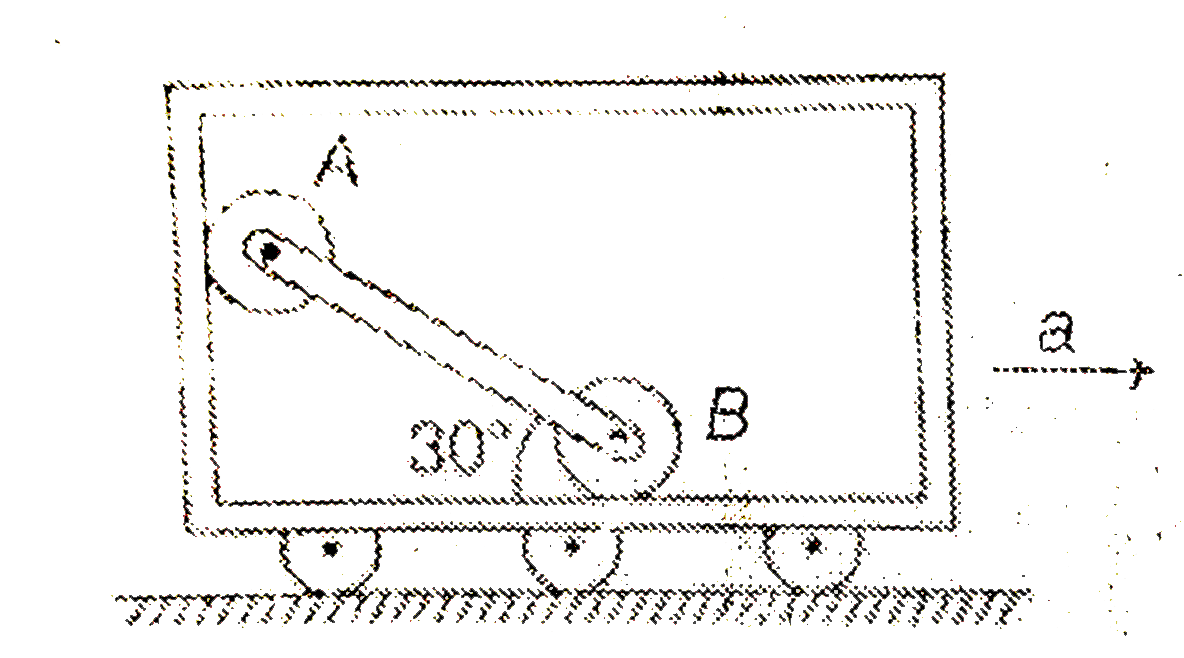
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A car is moving rightward with acceleration a=gsqrt(k)m//s^(2) . Find ...
Text Solution
|
- Neglect friction. Find acceleration of m, 2 m and 3 m as shown in the ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown neglecting friction and mass of pulley, what is th...
Text Solution
|
- The rod AB oriented parallel to the x^' axis of the reference frame K^...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of mass m is supported on two rollers each of mass m//2 ...
Text Solution
|
- Two cars A and B of equal masses (100 Kg) are moving on a straight hor...
Text Solution
|
- A car is moving rightward with acceleration a=gsqrt(k)m//s^(2) . Find ...
Text Solution
|
- A massless rod rigidly fixed at O. A sting carrying a mass m at one en...
Text Solution
|
- Find the acceleration of rod A and wedge B in the arrangement shown i...
Text Solution
|