Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
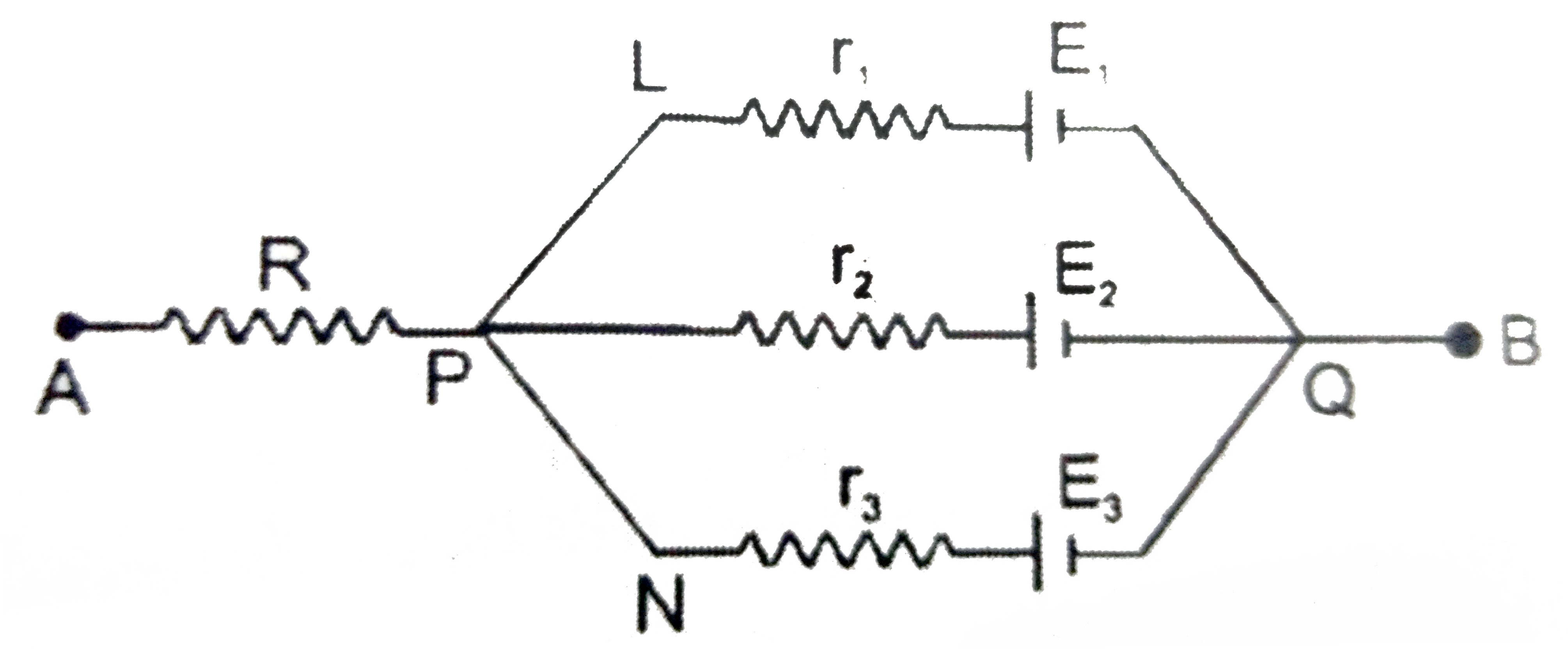
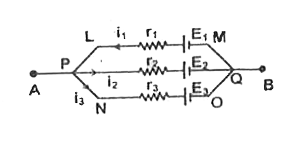
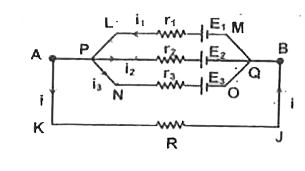
- In the circuit shown in fig. E(1)=3" volt",E(2)=2" volt",E(3)=1" vole ...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown here, E(1) = E(2) = E(3) = 2 V and R(1) = R(2) = ...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in fig. E(1)=3" volt",E(2)=2" volt",E(3)=1" vole ...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit as shown in figure, E(1)=2V , E(2)=2V, E(3)=1V, and R=r...
Text Solution
|
- In the following circuit E(1)=E(2)=E(3) 2V and R(1)=R(2)=AOmega . The ...
Text Solution
|
- चित्र में प्रदर्शित में E(1)=3 वोल्ट, E(3)=2 वोल्ट, E(3)=1 वोल्ट तथा R...
Text Solution
|
- दिखाइए गए परिपथ में, R(1)=1.0Omega,R(2)=2.0Omega,E(1)=2V और E(2)=E(3)=...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in fig. E(1)=3" volt",E(2)=2" volt",E(3)=1" vole ...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in figure ,(epsilon)(1)=3V,(epsilon)(2)=2V,(epsil...
Text Solution
|