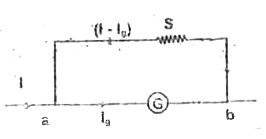
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A voltmeter has a range O - V with a series resistance R. With a serie...
Text Solution
|
- A voltmeter has a resistance G and range V. Calculate the resistance t...
Text Solution
|
- A voltmeter has a range O - V with a series resistance R . With a seri...
Text Solution
|
- एक वोल्ट्मीटर का प्रतिरोध G व परास V वोल्ट है। इस nV परास के वोल्ट्मीट...
Text Solution
|
- A voltmeter has resistance R0 and range V. What resistance should be c...
Text Solution
|
- A galvanometer has a resistance of G ohm and range of V volt. Calculat...
Text Solution
|
- A galvanometer has a resistance of G ohm and range of V volt. Calculat...
Text Solution
|
- A voltmeter has range 0 to V with a series resistance R. With a series...
Text Solution
|
- 10 V परास वाले वोल्टमीटर का प्रतिरोध 1000Omega है। इसका परास 100 V तक ...
Text Solution
|