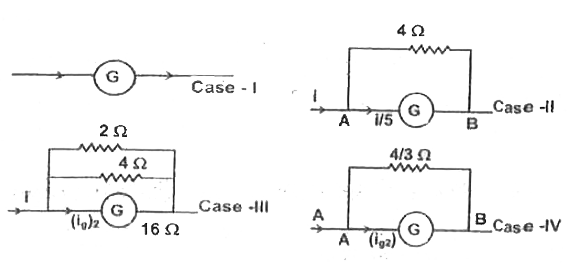
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Omega resistance, the deflectio...
Text Solution
|
- When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Omega resistance the deflection...
Text Solution
|
- A galvanometer shows a reading of 0.65 mA. When a galvanometer is shun...
Text Solution
|
- When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Omega resistance the deflection...
Text Solution
|
- When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4 Omega resistance, the deflecti...
Text Solution
|
- When a shunt of 4Omega is attahced to a galvanometer, the deflection r...
Text Solution
|
- The deflection in galvanometer falls to ((1)/(4))^(th) when it is shun...
Text Solution
|
- When a current of 1 Ampere is passed through a galvanometer coil, it i...
Text Solution
|
- When a galvanometer is shunted with a 6Omega resistance,the deflection...
Text Solution
|