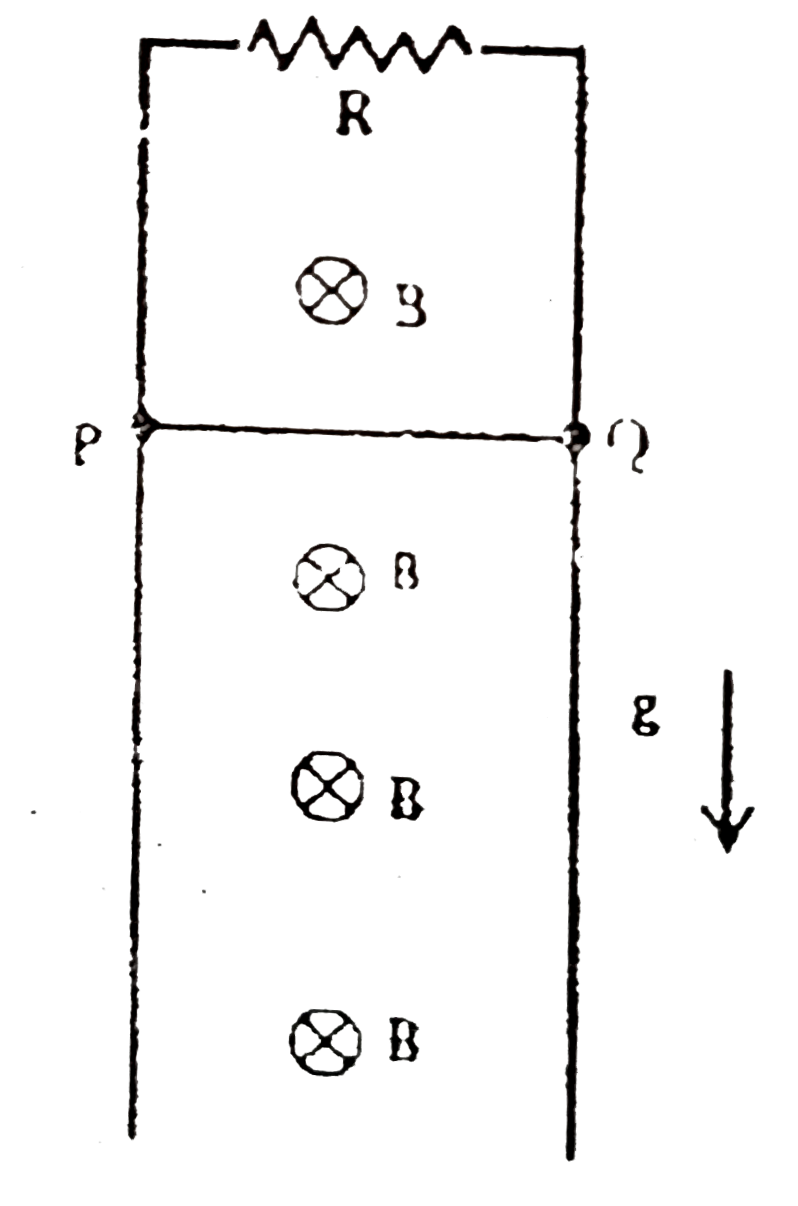
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A rod PQ mass 'm' and length l can slide without friction on two verti...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod of length 1 is moving on a horizontal smooth surface....
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of mass m and resistance R is sliding over the 2 conduc...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting bar mass m and length l moves on two frictionless paralle...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure, the pulley P moves to the right with a constant speed v...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure the pulley P moves to the right with a constant speed u....
Text Solution
|
- A rod PQ mass 'm' and length l can slide without friction on two verti...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure, the pulley P moves to the right with a constant speed u...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure, the pulley P moves to the right with a constant speed u...
Text Solution
|