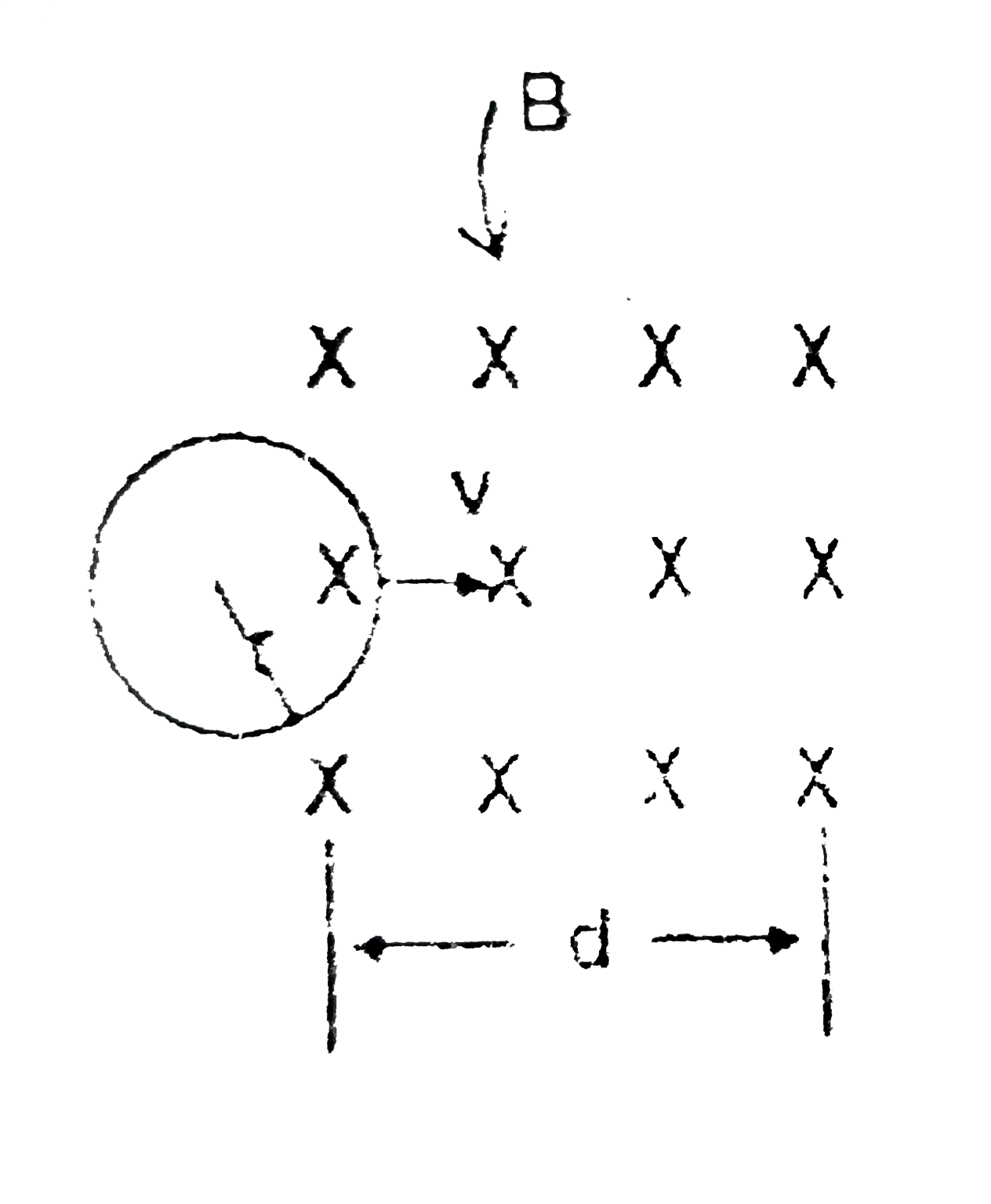A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A conducting loop is pulled with a constant velocity towards a region ...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting loop is pulled with a constant velocity towards a region ...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting loop is pulled with a constant velocity towards a region ...
Text Solution
|
- A triangular loop as shown in the figure is started to being pulled ou...
Text Solution
|
- A triangle loop as shown in the figure is started to being pulled out ...
Text Solution
|
- The endpoints of a conducting string (shaped as a circular loop) of co...
Text Solution
|
- एक आयताकार लूप और एक वृत्ताकार लूप एकसमान चुंबकीय क्षेत्र से क्षेत्रमु...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform circular loop of radius a and resistance R is pulled at a co...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting loop (as shown) has total resistance R. A uniform magneti...
Text Solution
|