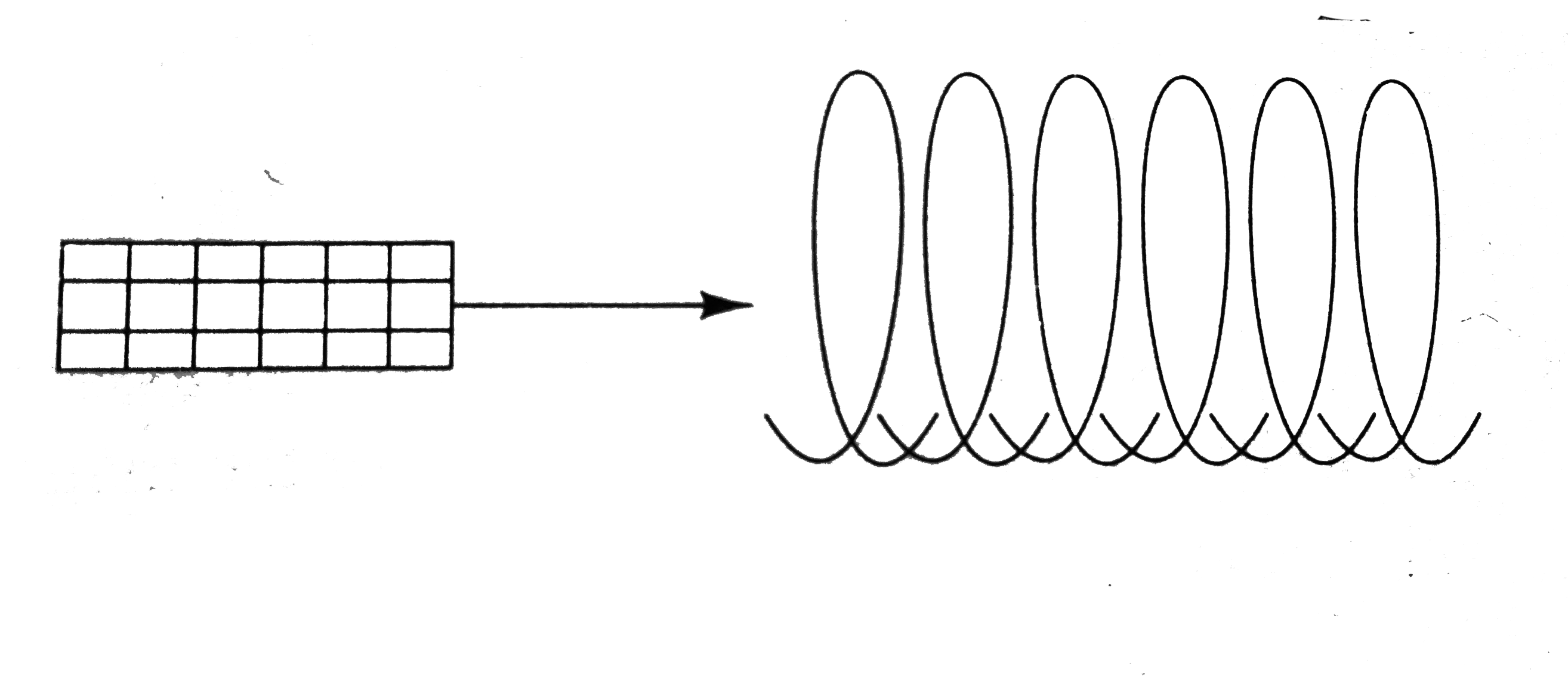
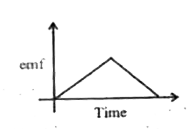
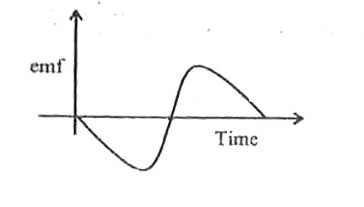
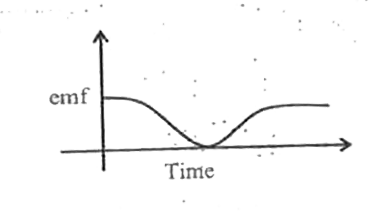
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A small bar magnet is being slowly inserted with constant velocity ins...
Text Solution
|
- A small bar magnet is being slowly inserted with constant velocity ins...
Text Solution
|
- Statement I: An emf is induced ina long solenoid by a bar magnet that ...
Text Solution
|
- The variation of induced emf (F) with time (t) in a coil if a short ba...
Text Solution
|
- Asseration: An emf is induced in a along solenoid by a bar magnet that...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : An induced emf is generated when magnet is withdrawn fro...
Text Solution
|
- A soft iron bar is inserted inside a current-carrying solenoid. The ma...
Text Solution
|
- If a bar magnet is moved inside a toroid, will there be any induced em...
Text Solution
|
- The variation of induced emf E with time t in a coil when a short bar ...
Text Solution
|