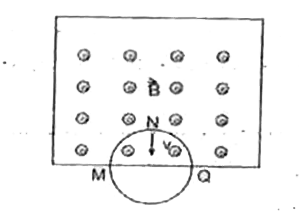
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A thin circular -conducting ring having N turns of radius R is falling...
Text Solution
|
- A thin semi-circular conducting ring of radius R is falling with its p...
Text Solution
|
- A vertical conducting ring of radius R falls vertically with a speed V...
Text Solution
|
- A vertical conducting ring ogradius R falls vertically in a horizontal...
Text Solution
|
- A thin semicircular conducting ring of radius R is falling with its pl...
Text Solution
|
- A thin semicircuilar conducting ring (PQR) of radius r is falling with...
Text Solution
|
- A thin semicircular conducting ring of radius R is falling with its pl...
Text Solution
|
- r त्रिज्या की एक पतली अर्धवृत्ताकार चालक रिंग (वलय) PQR किसी क्षैतिज ...
Text Solution
|
- एक अर्द्धवृत्ताकार वलय जिसकी त्रिज्या R है अपने तल के लम्बवत क्षैतिज च...
Text Solution
|