A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
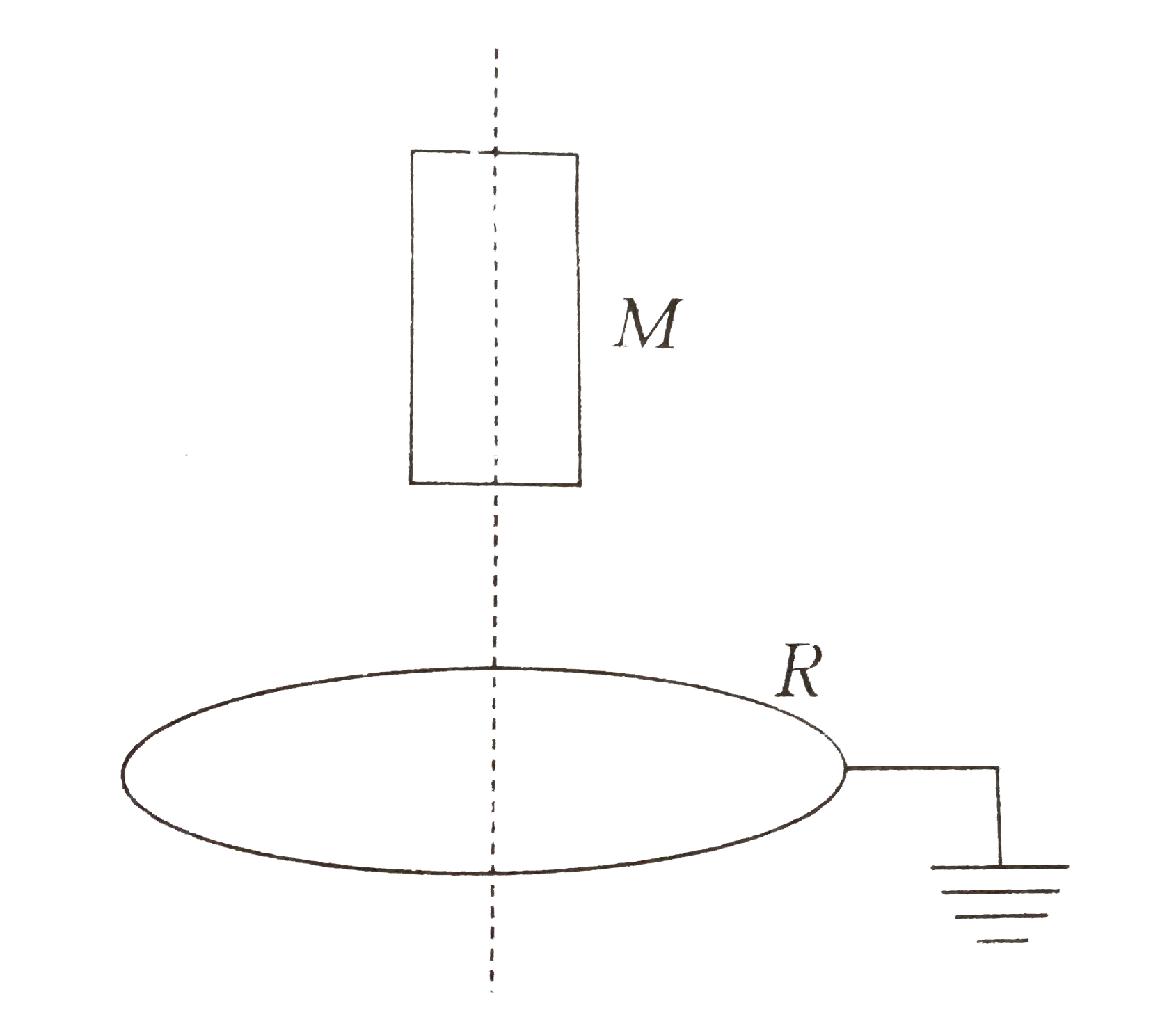
- A small magnet M is allowed to fall through a fixed horizontal conduct...
Text Solution
|
- A small magnet M is allowed to fall through a fixed horizontal conduct...
Text Solution
|
- A bar magnet falls through a material ring. Will its acceleration be e...
Text Solution
|
- A small magnet M is allowed to fall through a fixed horizontal conduct...
Text Solution
|
- A copper ring is held horizontally and a bar magnet is dropped through...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic ring with a small cut is held horizontally and a magnet is ...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic ring with a small cut is held horizontally and a magnet is ...
Text Solution
|
- A bar magnet is falling from some height through a metal ring. (i) Wil...
Text Solution
|
- एक छोटा चुम्बक एक स्थिर क्षैतिज वलय R पर गिरती है। माना गुरुत्वीय त्वर...
Text Solution
|