Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
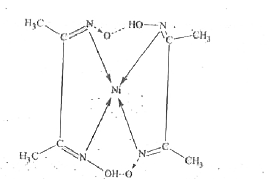
- NiCl(2) in the presence of dimethyl glyoxime (DMG) gives a complex wit...
Text Solution
|
- NiCI(2) in the presence of dimethy1 glyoxime (DMG) gives a complex whi...
Text Solution
|
- Dimethyl glyoxime gives a red precipitate with Ni^(2+), which is used ...
Text Solution
|
- A metal salt solution when treated with dimethyl glyoxime and NH(4)OH ...
Text Solution
|
- When diemethyl glyoxime is added to the aqueous solution of nickel (II...
Text Solution
|
- Dimethyl glyoxime is added to alcoholic solution of NiCl(2) . When amm...
Text Solution
|
- [Ni(NH)(4)]^(2-) is diamagnetic but [NiCl(4)]^(2-) is paramagnetic. Gi...
Text Solution
|
- डाइमेथेल ग्लाइओक्सिम की उपस्थिति में NiCl(2) एक संकर बनाता है जो NH(4)...
Text Solution
|
- डाइमेथेल ग्लाइओक्सिम की उपस्थिति में NiCl(2) एक संकर बनाता है जो NH(4)...
Text Solution
|