Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
OMEGA PUBLICATION-CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS -MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
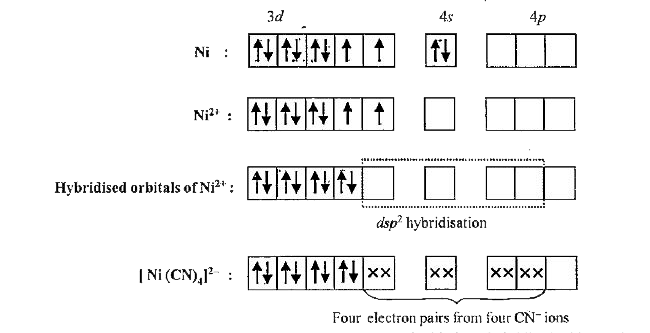
- With the help of valence bond theory expiaiil that tetracyanonickelate...
Text Solution
|
- An example of double salt is
Text Solution
|
- Write IUPAC name of [Co(NH3)6]Cl3.
Text Solution
|
- Name of complex [pt(NH3)6]Cl4 is
Text Solution
|
- [Co(NH3)5 Br]SO4 and [Co(NH3)5 SO4] Br areexamples of which type of i...
Text Solution
|
- Which complex has square planar structure?
Text Solution
|
- The number of d-electrons in [Cr(H2O)6]^(3+) (at. No. of Cr = 24 ) is
Text Solution
|
- The oxidation number of iron in K4[Fe (CN)6] is :
Text Solution
|
- The IUPAC name of [Co(Cl) (NO2) (en)2 ] Cl is
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following complex species involves d^2sp^3 hybridisation ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following acts as a positive ligand?
Text Solution
|
- The co-ordination number of Cr in [Cr(NH3)3(H2O)3]Cl3 is
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic moment of [Ni(CO4)] is
Text Solution
|
- The effective atomic number of Cr (Atomic no. = 24) in [Cr (NH3)6]Cl3 ...
Text Solution
|
- The effective atomic number of Fe in Fe(CO)5 is
Text Solution
|
- The coordination number of copper in cuprammonium sulphate is
Text Solution
|
- en is an example of a
Text Solution
|
- Ferrocene is
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following ligands is expected to be bidentate?
Text Solution
|
- The number of unpaired electrons in the complexes [NiCl4]^(-2) and [Ni...
Text Solution
|
- According to effective atomic number, the central metal acquires
Text Solution
|