Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ACCURATE PUBLICATION-BOARD PAPER MARCH - 2019-QUESTIONS
- Write the IUPAC name of following : [Cr(NH3)3 (H2O)3]Cl3
Text Solution
|
- A compound X and Y crystallises in the cubic structure in which Y atom...
Text Solution
|
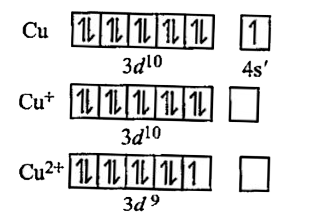
- Why Cu(l) is colourless and Cu(ll) is blue in colour ?
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant for a first order reaction Is 90 s^-1 .How much time...
Text Solution
|
- Define ore and minerals.
Text Solution
|
- Give monomers name and preparation of Nylon 6,6.
Text Solution
|
- All three classes of aliphatic amines are stronger bases tha ammonia. ...
Text Solution
|
- Write chemical name, deficiency disease and one source of vitamin-C.
Text Solution
|
- 18 g of glucose is dissolved in 1 kg of water. At what temperature wil...
Text Solution
|
- State Henry's law and mention its some important applications.
Text Solution
|
- Why bond angle of Phosphine (PH3) is less than Ammonia (NH3) ?
Text Solution
|
- Why is H2S less acidic than H2 Te ?
Text Solution
|
- The molar conductivities at infinite dilution for sodium acetate, hydr...
Text Solution
|
- What is corrosion?
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the molar conductance of solutions of MgCl2 at infinite dil...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Give two differences between emf and potential difference. (ii) ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain Reimer Tiemann reaction with one example.
Text Solution
|
- How will you convert chlorobenzene into phenol ?
Text Solution
|
- Why Phenols are more acidic than Alcohol ?
Text Solution
|
- Write two differences between physical adsorption and chemical adsorpt...
Text Solution
|