Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ACCURATE PUBLICATION-BOARD PAPER MARCH - 2019-QUESTIONS
- Give one difference between crystalline and amorphous solids.
Text Solution
|
- An element having a density 11.2"g cm"^(-3) forms a fcc lattice with e...
Text Solution
|
- Define unit cell and paramagnetic substance.
Text Solution
|
- Write the following reaction: Wurtz Fittig Reaction
Text Solution
|
- True/False- Stems absorb water and minerals from the soil.
Text Solution
|
- True/False- The plant gets nitrogen from air.
Text Solution
|
- Why solubility of Haloalkanes in water is very low ?
Text Solution
|
- Give one use of freon.
Text Solution
|
- Why nitrogen is important for the plants?
Text Solution
|
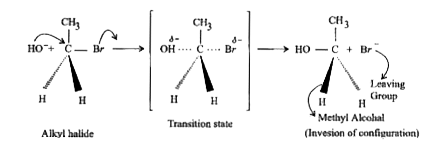
- Give the mechanism of substitution nucleophilic bimolecular, SN^2 reac...
Text Solution
|
- Define Optical activity.
Text Solution
|
- Why SF6 is known but SH6 is not known ?
Text Solution
|
- From HF and Hl which is more acidic and why ?
Text Solution
|
- Give preparation of XeF6 and XeOF2.
Text Solution
|
- True/False- The ovary is found in the stamen.
Text Solution
|
- How many unpaired electrons are present in Fe^+3 and Zn^+2.
Text Solution
|
- Why is La(OH)3 more basic than Lu(OH)3 ?
Text Solution
|
- Give preparation of Potassium Permanganate (KMnO4).
Text Solution
|
- What is Lanthanide contraction ? What is the cause and consequences of...
Text Solution
|
- Why transition metals show catalytic properties?
Text Solution
|